Best weight training routine for women to build lean muscle? Forget the bulky bodybuilder image! This isn’t about becoming a human barbell; it’s about sculpting a stronger, leaner, more confident YOU. We’re diving deep into a program designed to help women build lean muscle mass, boosting metabolism, enhancing strength, and improving overall well-being. Prepare to ditch the fluff and embrace the power of purposeful weight training – because strong is the new skinny (and way more fun!).
This guide will unpack the physiological differences between men’s and women’s muscle growth, explaining why a tailored approach is key. We’ll reveal the secrets to crafting a killer workout plan, focusing on effective exercises, proper form, and strategic progression. Get ready to learn about the perfect balance of compound and isolation exercises, the magic of progressive overload, and the crucial role of nutrition and rest in maximizing your results.
We’ll even tackle common pitfalls and offer modifications for various fitness levels, ensuring this program works for you, no matter where you’re starting.
Introduction
Let’s ditch the outdated idea that weight training is only for bulky bodybuilders! For women, strength training is a total game-changer, offering a pathway to a healthier, stronger, and more confident you. We’re talking about building lean muscle, not looking like a linebacker (unless that’s your goal, of course!). This introduction will unravel the fascinating world of lean muscle growth specifically for women, highlighting the unique physiological aspects and the incredible benefits it brings.There are some key physiological differences between how men and women build muscle.
Men generally have higher levels of testosterone, the hormone primarily responsible for muscle growth. This doesn’t mean women can’t build impressive muscle; it simply means the process might look a little different and require a slightly different approach. Women tend to build muscle with more of a focus on endurance and definition, often resulting in a leaner, more toned physique.
Lean Muscle Mass Benefits for Women
Lean muscle mass is your friend. It’s not just about aesthetics; it’s a cornerstone of overall health and well-being. Increased lean muscle mass boosts your metabolism, meaning you burn more calories even at rest. This helps with weight management and can significantly reduce the risk of developing conditions like type 2 diabetes. Beyond that, stronger muscles improve bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis, a serious concern for women as they age.
Furthermore, increased muscle strength translates to improved posture, reduced back pain, and enhanced daily functionality – making everything from carrying groceries to playing with your kids easier and more enjoyable. Imagine effortlessly lifting your suitcase onto the overhead compartment on your next vacation – that’s the power of lean muscle!
Defining Lean Muscle
So, what exactlyis* lean muscle? Think of it as muscle tissue with a lower percentage of body fat. It’s about building strong, defined muscles without excessive bulk. This contrasts with bulk muscle gain, which often involves a higher body fat percentage and a more significantly increased muscle mass. Lean muscle is achieved through a combination of consistent weight training and a balanced diet.
It’s about sculpting your physique, not just increasing its size. The result is a strong, toned, and healthy body that looks and feels amazing. Think dancer’s physique versus powerlifter’s physique – both are strong, but the aesthetic is different. Lean muscle is more about the sculpted look, emphasizing definition and strength.
Essential Exercises for Lean Muscle Development
Building lean muscle as a woman is all about smart training and a dash of sassy determination. Forget the myth of bulky muscles – with the right exercises, you’ll sculpt a strong, toned physique that’ll make you feel amazing. This isn’t about becoming a bodybuilder; it’s about enhancing your strength, improving your posture, and boosting your overall well-being. Think of it as adding some serious sparkle to your already awesome self.
A Beginner’s Weight Training Routine
This routine focuses on compound movements (working multiple muscle groups simultaneously) and isolation exercises (targeting specific muscles). Remember, proper form is key! Start with lighter weights and focus on mastering the technique before increasing the load. Consistency is your secret weapon; aim for at least two sessions per week, allowing for rest days in between.
| Exercise | Muscle Group | Sets | Reps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squats | Quads, Glutes, Hamstrings | 3 | 10-12 |
| Push-ups (modified on knees if needed) | Chest, Triceps, Shoulders | 3 | 8-10 |
| Dumbbell Rows | Back, Biceps | 3 | 10-12 |
| Overhead Press (dumbbells or barbell) | Shoulders, Triceps | 3 | 8-10 |
| Bicep Curls (dumbbells) | Biceps | 3 | 12-15 |
| Triceps Extensions (dumbbells or cable machine) | Triceps | 3 | 12-15 |
| Plank | Core | 3 | 30-60 seconds hold |
Upper Body Strength Routine
This routine focuses on building upper body strength and definition. Remember to choose a weight that challenges you without compromising your form. Think quality over quantity – controlled movements are your friends.
| Exercise | Muscle Group | Sets | Reps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bench Press (barbell or dumbbells) | Chest, Triceps, Shoulders | 3 | 8-12 |
| Overhead Press (barbell or dumbbells) | Shoulders, Triceps | 3 | 10-15 |
| Bent-Over Rows (barbell or dumbbells) | Back, Biceps | 3 | 10-15 |
| Lateral Raises (dumbbells) | Shoulders | 3 | 12-15 |
| Triceps Pushdowns (cable machine) | Triceps | 3 | 15-20 |
| Bicep Curls (dumbbells or barbell) | Biceps | 3 | 15-20 |
Lower Body Strength Routine
This routine is designed to target your glutes, hamstrings, and quads – the powerhouses of your lower body. Feel the burn (in a good way!), and remember to engage your core throughout each exercise for optimal results and injury prevention.
| Exercise | Muscle Group | Sets | Reps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barbell Squats | Quads, Glutes, Hamstrings | 3 | 8-12 |
| Romanian Deadlifts (RDLs) | Hamstrings, Glutes | 3 | 10-15 |
| Lunges (alternating legs) | Quads, Glutes, Hamstrings | 3 | 10-12 per leg |
| Glute Bridges | Glutes, Hamstrings | 3 | 15-20 |
| Calf Raises | Calves | 3 | 15-20 |
Core Strengthening Exercises, Best weight training routine for women to build lean muscle
A strong core is essential for stability, posture, and overall fitness. These exercises will help you build a rock-solid midsection. Remember to maintain proper form to avoid strain.A strong core is like the foundation of a house – crucial for stability and overall structural integrity. These exercises will help build that strong core.
| Exercise | Muscle Group | Sets | Reps/Hold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plank | Abdominals, lower back | 3 | 30-60 seconds hold |
| Crunches | Abdominals | 3 | 15-20 |
| Russian Twists (with or without weight) | Obliques | 3 | 15-20 per side |
| Bicycle Crunches | Abdominals, obliques | 3 | 15-20 per side |
Workout Program Structure and Progression
Building lean muscle isn’t a sprint; it’s a marathon with plenty of strategically placed snack breaks (think protein shakes!). Consistency and smart progression are key, especially for women who often respond differently to training than men. Ignoring this crucial aspect is like trying to build a skyscraper with a toothpick – it’s just not going to happen.Progressive overload is the secret sauce to sculpting that enviable physique.
Essentially, it means gradually increasing the demands you place on your muscles over time. This forces them to adapt, grow stronger, and, most importantly, build more lean muscle mass. Think of it as a constant challenge for your muscles – keep them guessing, and they’ll keep growing.
Progressive Overload Explained
Progressive overload isn’t about lifting the heaviest weight possible right away; it’s a carefully planned ascent. You can increase the challenge in several ways: increasing the weight you lift, increasing the number of repetitions you perform, increasing the number of sets, or decreasing your rest time between sets. Finding the right balance is crucial. A good starting point is to aim for a weight that allows you to complete your target reps with good form, but leaves you feeling challenged by the last few.
Adjusting Weight and Reps for Continuous Progress
Let’s say you’re doing squats. You start with 10 reps of 50 pounds for 3 sets. After a few weeks, those 10 reps feel easy. You have several options: you could increase the weight (perhaps to 55 pounds and aim for 8-10 reps), increase the reps (12-15 reps with 50 pounds), add another set, or shorten your rest time between sets.
The key is to make small, manageable increases. If you jump to a weight that’s too heavy too soon, you risk injury and burnout – nobody wants that. Listen to your body and don’t be afraid to scale back if needed.
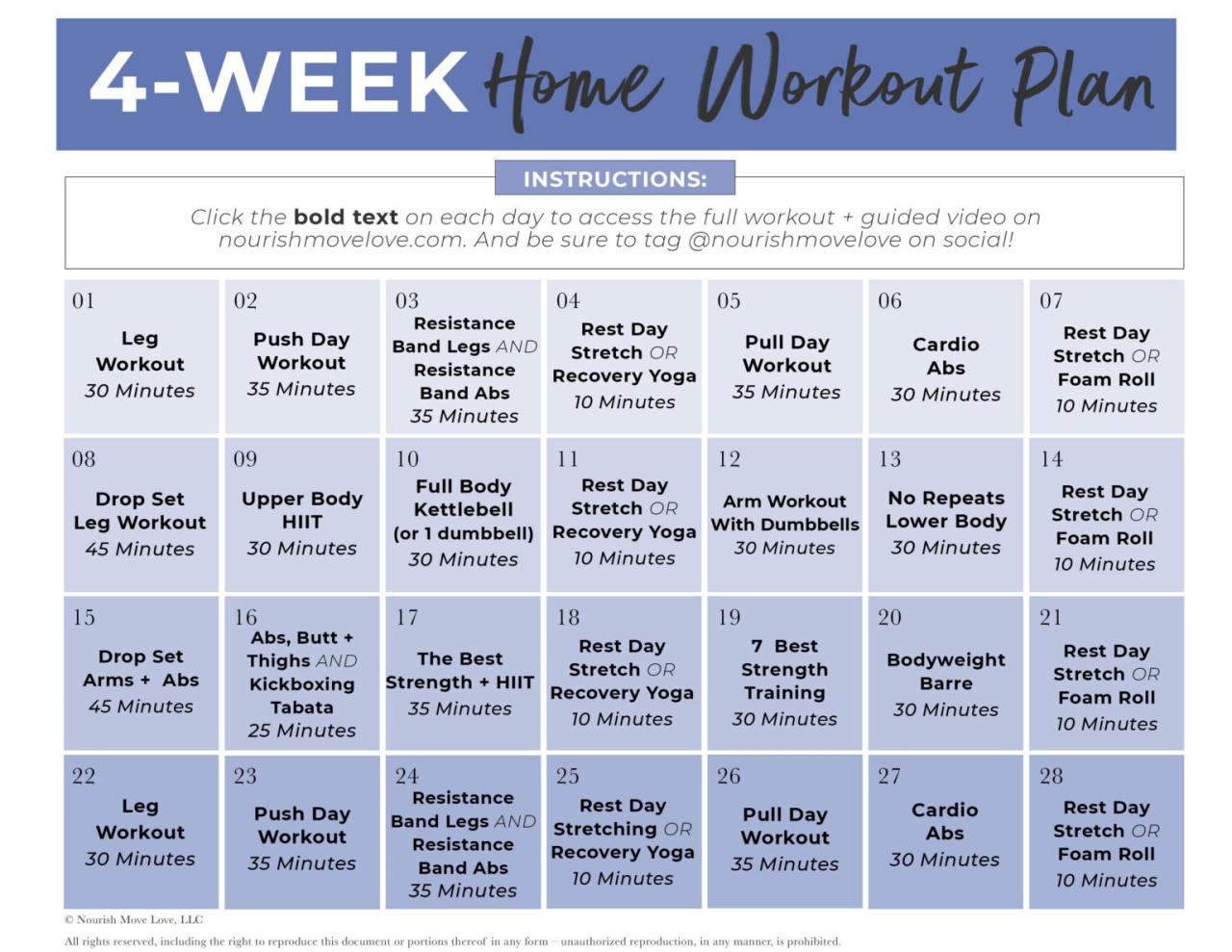
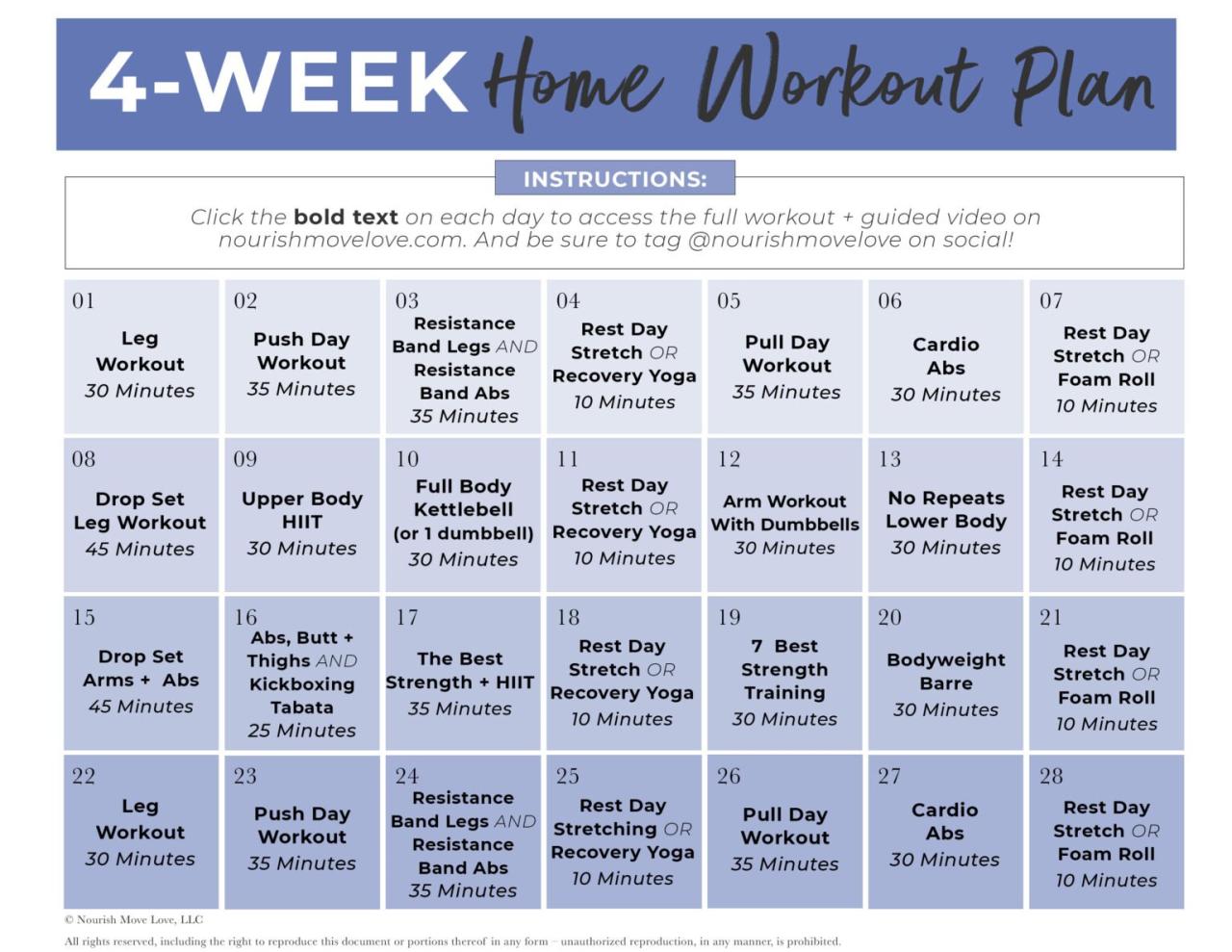
A 12-Week Progressive Weight Training Program
This program is a sample, and should be adjusted to your fitness level and experience. Remember to prioritize proper form over lifting heavy weights.
| Week | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 | Day 6 | Day 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-4 (Beginner) | Upper Body (lighter weights, higher reps) | Rest | Lower Body (lighter weights, higher reps) | Rest | Core | Rest | Rest |
| 5-8 (Intermediate) | Upper Body (moderate weight, moderate reps) | Rest | Lower Body (moderate weight, moderate reps) | Rest | Core & Cardio | Rest | Rest |
| 9-12 (Advanced) | Upper Body (heavier weight, lower reps) | Rest | Lower Body (heavier weight, lower reps) | Rest | HIIT & Core | Rest | Active Recovery (light walk) |
Note: Each workout should include a warm-up and cool-down. Focus on compound exercises (like squats, deadlifts, bench press, overhead press, rows) to work multiple muscle groups simultaneously. For example, Week 1-4, a beginner might do 2 sets of 12-15 reps for each exercise, while an advanced lifter might do 3-4 sets of 6-8 reps.
Program Modifications for Different Fitness Levels
Beginner: Start with bodyweight exercises or very light weights, focusing on perfect form. Aim for higher repetitions (12-15) and fewer sets (2-3). Prioritize learning the correct technique before increasing the weight. Think of it as building a strong foundation for your muscle skyscraper. Intermediate: Increase the weight and decrease the repetitions (8-12).
Add more sets (3-4). Incorporate more challenging variations of exercises. For example, you might progress from regular push-ups to incline push-ups to decline push-ups. Advanced: Use heavier weights and lower repetitions (6-8). Incorporate advanced training techniques like drop sets, supersets, and rest-pause sets.
Consider adding plyometrics or other advanced exercises to further challenge your muscles.
Nutrition for Lean Muscle Gain

Building lean muscle isn’t just about lifting weights; it’s a delicious dance with your diet! Think of your body as a high-performance sports car – you wouldn’t put regular unleaded in a Ferrari, would you? Similarly, fueling your body with the right nutrients is crucial for optimal muscle growth and overall well-being. Let’s explore the nutritional trifecta that will help you sculpt that amazing physique.
Macronutrients – protein, carbohydrates, and fats – are the building blocks of a successful muscle-building diet. Getting the right balance is essential, like finding the perfect harmony in a symphony orchestra. Too much of one and not enough of another, and your progress will sound more like a cacophony than a masterpiece.
Macronutrient Balance for Muscle Growth
The ideal macronutrient ratio varies depending on individual factors like activity level, genetics, and goals. However, a general guideline for women aiming to build lean muscle is to prioritize protein, followed by carbohydrates, and then healthy fats. Imagine protein as the bricks, carbohydrates as the mortar, and healthy fats as the architectural design that holds it all together beautifully.
A common suggestion is a range of 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, 40-50% of your total daily calories from carbohydrates, and 20-30% from healthy fats. This isn’t a rigid formula, but rather a flexible framework to guide your nutritional choices. Remember, consistency is key!
Protein-Rich Foods for Women
Protein is the star of the muscle-building show. It provides the amino acids your body needs to repair and build muscle tissue after your intense workouts. Think of it as the ultimate muscle-mending magic potion!
- Lean meats: Chicken breast, turkey breast, lean beef – these are classic choices for a reason. They’re packed with protein and relatively low in fat.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, and cod are excellent sources of protein and healthy omega-3 fatty acids. A win-win!
- Eggs: A complete protein source, eggs are versatile and easy to incorporate into various meals. Think omelets, frittatas, or even just a simple boiled egg.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and beans are fantastic vegetarian sources of protein and fiber. They also contribute to a well-rounded diet.
- Greek Yogurt: Higher in protein than regular yogurt, Greek yogurt is a delicious and convenient snack or breakfast option.
The Role of Carbohydrates in Fueling Workouts and Muscle Recovery
Carbohydrates are your body’s primary energy source, especially during intense workouts. They’re the fuel that powers your lifts and keeps you going strong. Think of them as the high-octane fuel for your muscle-building engine.
Choosing complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, over refined carbohydrates like white bread and sugary drinks, is crucial for sustained energy levels and preventing energy crashes. These complex carbs provide a slower, more steady release of energy, preventing those dreaded mid-workout slumps.
Want sculpted arms and a backside that’ll make heads turn? The best weight training routine for women to build lean muscle involves dedication and the right plan. Finding the perfect program can feel like searching for the Holy Grail, but thankfully, resources like the best strength training program website are out there to guide you. With a solid plan, you’ll be well on your way to achieving your fitness goals and feeling amazing.
So ditch the excuses and start sculpting that dream physique!
The Importance of Healthy Fats for Hormone Regulation and Overall Health
Healthy fats are often misunderstood, but they play a vital role in hormone production, nutrient absorption, and overall health. They’re not the enemy; they’re essential components of a balanced diet. Think of them as the lubrication that keeps your body’s machinery running smoothly.
Incorporate sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil into your diet. These healthy fats contribute to hormone regulation, which is crucial for muscle growth and overall well-being. They also keep your skin glowing and your hair shining. A bonus!
Recovery and Rest: Best Weight Training Routine For Women To Build Lean Muscle

Building lean muscle isn’t just about grueling workouts; it’s a delicate dance between pushing your limits and allowing your body to rebuild stronger. Think of it like baking a magnificent muscle cake – you need the right ingredients (training), the perfect temperature (nutrition), and crucially, the ideal baking time (recovery). Neglecting recovery is like leaving your cake in the oven too long – you’ll end up with a burnt, brittle mess, not the sculpted masterpiece you envisioned.Sleep is the unsung hero of muscle recovery.
During deep sleep, your body releases growth hormone, a crucial player in muscle repair and growth. Skimping on sleep is like giving your muscles a half-hearted pat on the back instead of a full-body massage. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night; consider it your mandatory muscle-building meditation.
Sleep’s Role in Muscle Recovery and Growth
Sufficient sleep allows your body to effectively repair muscle tissue damaged during weight training. Studies have shown a strong correlation between adequate sleep and increased muscle protein synthesis, the process by which your muscles build and repair themselves. Lack of sleep, on the other hand, can lead to impaired muscle protein synthesis, hindering your progress and potentially increasing the risk of injury.
Imagine trying to build a skyscraper with a crew that’s chronically sleep-deprived – it’s a recipe for disaster!
Benefits of Active Recovery
Active recovery isn’t about hitting the gym again full force; it’s about gentle movement that promotes blood flow and reduces muscle soreness. Think light cardio, such as a leisurely walk or a gentle swim, or stretching to increase flexibility and range of motion. Active recovery can help flush out metabolic waste products from your muscles, reducing stiffness and soreness, allowing you to bounce back faster for your next workout.
Consider it a preemptive strike against muscle fatigue, helping you to stay ahead of the game.
Importance of Rest Days
Rest days are not lazy days; they’re essential for preventing overtraining and injuries. Your muscles need time to recover and rebuild, and pushing them relentlessly without adequate rest will lead to plateaus, injuries, and burnout. Scheduling regular rest days allows your body to adapt to the stress of training, maximizing your gains while minimizing the risk of injury.
Think of your muscles as delicate seedlings – they need time to grow strong roots before you can expect them to bear fruit.
Relaxation Techniques for Stress Management
Stress hormones can hinder muscle recovery and growth. Incorporating relaxation techniques into your routine can help manage stress levels and promote recovery. Examples include deep breathing exercises, yoga, meditation, or simply spending time in nature. These techniques help lower cortisol levels (the stress hormone), creating a more favorable environment for muscle repair and growth. Imagine your muscles as delicate flowers – they need a calm, nurturing environment to blossom.
Regular relaxation practices are like providing them with the perfect sunshine and gentle rain.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
So, you’re ready to sculpt your physique like a Greek goddess (minus the questionable sandals)? Fantastic! But before you hoist those dumbbells like you’re single-handedly lifting the weight of the world, let’s address some common pitfalls that can hinder your progress—or worse, lead to injury. We’re talking about those sneaky little mistakes that even seasoned lifters can fall prey to.
This isn’t about fear-mongering; it’s about empowering you with knowledge so you can train smarter, not harder.Proper form and technique are paramount in weight training, especially for women. Think of your body as a finely tuned machine; improper form is like throwing sand in the gears. It not only reduces the effectiveness of your workout but significantly increases your risk of injury.
We’re not aiming for “good enough”; we’re aiming for “perfectly executed” (or as close as humanly possible!). This involves understanding the correct movement patterns for each exercise, engaging the right muscle groups, and maintaining proper posture throughout.
Improper Form and Technique
Ignoring proper form is like trying to bake a cake without measuring ingredients – you might getsomething*, but it won’t be the masterpiece you envisioned. Incorrect form compromises muscle activation, reduces the effectiveness of your workout, and dramatically increases the risk of injury. For example, performing squats with rounded back puts excessive stress on your spine, potentially leading to back pain or even more serious injuries.
Similarly, improper deadlift form can strain your lower back, hamstrings, or even your shoulders. Investing time in learning correct form from a qualified trainer or reputable online resources is an investment in your long-term health and fitness goals. Visualize the movement before you begin, focus on controlled movements, and don’t be afraid to start with lighter weights to perfect your technique.
Overtraining
Overtraining is the fitness equivalent of a burnout. Your body needs time to recover and rebuild after intense workouts. Ignoring this crucial aspect can lead to a plateau in your progress, decreased performance, increased risk of injury, and even burnout. Symptoms of overtraining include persistent muscle soreness, fatigue, decreased motivation, poor sleep, and even mood changes. If you notice these signs, don’t power through it; listen to your body.
Reduce the intensity or frequency of your workouts, prioritize rest and recovery, and consider incorporating active recovery methods like light cardio or yoga. Remember, progress isn’t linear; it’s a marathon, not a sprint. Think of it like this: a perfectly sculpted physique isn’t built in a day, and neither is a healthy relationship with fitness.
Ignoring Your Body’s Signals
Your body is incredibly intelligent. It’s constantly communicating with you, sending signals about fatigue, pain, and the need for rest. Ignoring these signals is a recipe for disaster. Persistent pain, especially sharp or stabbing pain, should never be ignored. It’s a clear indication that something is wrong, and continuing to train through pain can lead to serious injury.
Listen to your body’s whispers before they turn into screams. If you experience pain, stop the exercise immediately. Rest, ice the affected area, and seek professional advice if needed. Remember, modifying or adjusting your routine based on your body’s needs is a sign of intelligence, not weakness. It’s about sustainable progress, not pushing through pain for the sake of a fleeting sense of accomplishment.
Addressing Individual Needs and Considerations
Building a lean, mean, muscle-machine is a fantastic goal, but remember, one size doesn’t fit all – especially when it comes to weight training. Your journey should be as unique as you are, tailored to your specific aspirations and physical capabilities. Let’s explore how to customize your routine for optimal results.Individual goals significantly influence your weight training program.
Are you aiming for peak strength, a sculpted physique, or shedding those extra pounds? Each goal requires a different approach to exercise selection, intensity, and volume. For example, a strength-focused program emphasizes heavier weights and lower repetitions, while a toning program might use lighter weights with higher repetitions and a focus on muscular endurance. Weight loss often incorporates both strength training and cardiovascular exercise.
Goal-Specific Program Adjustments
Tailoring your workout to your specific goal is key. For strength, focus on compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses with heavier weights and fewer repetitions (3-5 sets of 3-5 reps). For toning, prioritize higher repetitions (12-15 reps) with lighter weights and a focus on controlled movements. If weight loss is your primary aim, combine strength training with regular cardio for optimal calorie burning and metabolic boost.
Remember, consistency is crucial regardless of your chosen focus. A well-structured plan, even if followed less intensely, is far superior to an ambitious plan abandoned after a week.
Modifications for Women with Specific Health Conditions or Limitations
Many women have pre-existing health conditions or physical limitations that require modifications to their weight training routines. For example, women with arthritis might benefit from using lighter weights and focusing on exercises with less joint stress, such as swimming or cycling, alongside modified weight training. Those with back problems should prioritize core strengthening exercises and avoid movements that exacerbate pain.
Pregnant women need to adjust their workouts based on their trimester and consult their physician before making any significant changes. It’s crucial to listen to your body and modify or stop an exercise if you experience pain.
Importance of Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before embarking on any new exercise program, consulting a healthcare professional is paramount. They can assess your overall health, identify any potential risks, and provide personalized recommendations based on your medical history. This is especially important for women with pre-existing conditions like heart disease, diabetes, or osteoporosis. A doctor can help you safely navigate your fitness journey and prevent potential injuries.
Don’t consider this a mere formality; it’s an investment in your well-being.
Finding a Qualified Personal Trainer or Fitness Professional
A qualified personal trainer can be invaluable in creating a safe and effective weight training program tailored to your individual needs and goals. They can assess your current fitness level, teach you proper form to prevent injuries, and provide motivation and support. Look for trainers with certifications from reputable organizations, such as the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) or the National Strength and Conditioning Association (NSCA).
Consider asking for referrals from friends or your doctor and scheduling consultations with a few trainers before making a decision. Remember, finding the right trainer is like finding the right pair of shoes – comfort and a good fit are crucial for a successful partnership.
Ultimate Conclusion
So, there you have it – your roadmap to lean muscle mastery! Remember, building lean muscle is a journey, not a race. Embrace the process, celebrate your progress, and don’t be afraid to adjust the plan as needed. Listen to your body, fuel it right, and watch as you transform your strength, your physique, and your confidence. Get ready to unleash your inner Amazon – because you’ve got this!