Best Weightlifting Routine for building strength and losing weight? Think less “grunting gym bro” and more “sculpted superhero.” This isn’t your grandpappy’s weightlifting; we’re talking about a scientifically-sound program that’ll help you shed pounds and pack on muscle simultaneously. Prepare for a journey of iron-pumping awesomeness, where sweat becomes your sparkle and gains are your glorious reward. We’ll delve into the magical world of compound exercises, master the art of progressive overload (it’s less scary than it sounds!), and even decipher the cryptic language of macronutrients.
Get ready to unleash your inner weightlifting warrior!
We’ll cover everything from understanding the physiological magic behind muscle growth and fat loss to designing a 12-week program that’s as effective as it is enjoyable. We’ll tackle nutrition strategies that fuel your workouts and help you achieve your goals, plus learn how to stay motivated, prevent injuries, and adjust your routine as you progress. Think of it as your personal weightlifting sherpa, guiding you to the peak of physical fitness (with maybe a few hilarious anecdotes along the way).
Understanding the Fundamentals of Strength Training and Weight Loss
So, you want to sculpt a physique that would make Michelangelo weep with envy while simultaneously shedding those extra pounds? Excellent! Building muscle and losing fat simultaneously is totally achievable, but it requires a nuanced understanding of how your body works. Think of it as a finely tuned engine – you need the right fuel (food), the right maintenance (training), and the right driving instructions (programming) to get optimal results.
The magic happens at the cellular level. Strength training stimulates muscle protein synthesis, essentially building new muscle tissue. This process requires energy, and that energy comes from your calorie intake. Simultaneously, your body burns calories for various metabolic processes, including the energy expenditure associated with building muscle. To lose fat, you need to create a calorie deficit – meaning you burn more calories than you consume.
However, a drastic calorie deficit can hinder muscle growth, hence the delicate balance.
Physiological Processes of Muscle Building and Fat Burning
Muscle growth (hypertrophy) occurs when the rate of muscle protein synthesis exceeds the rate of muscle protein breakdown. This is stimulated by progressive overload in your weight training – consistently challenging your muscles with heavier weights or more reps. Fat burning, on the other hand, is largely governed by energy balance. When you consume fewer calories than your body expends, it taps into stored fat reserves for energy.
The key is to find a balance where you’re building muscle while also creating a slight calorie deficit. This is often achieved through a combination of strategic nutrition and smart training. Imagine it like this: your muscles are like a sponge soaking up the nutrients you provide while your body’s furnace is steadily burning fat for fuel.
Calorie Intake, Macronutrient Distribution, and Weight Loss
The equation is simple, yet often tricky to master: Calories In < Calories Out = Weight Loss. However,
-what* those calories are is crucial. Macronutrients – proteins, carbohydrates, and fats – play different roles. Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth; carbohydrates provide energy for workouts; and fats support hormone production and overall health. A typical recommendation for weight loss and muscle building is to prioritize protein intake (around 1 gram per pound of body weight), maintain moderate carbohydrate intake (adjusting based on activity levels), and consume healthy fats. Remember, a drastic reduction in calories can lead to muscle loss and a slower metabolism. Think of it as a marathon, not a sprint. Small, sustainable changes are key. For example, consider someone who consumes 2500 calories daily and burns 2000. By reducing their intake to 2200 and maintaining their activity, they create a 200-calorie deficit daily, leading to gradual weight loss.
Training Styles and Their Suitability for Strength and Weight Loss
Different training styles cater to different goals. Powerlifting focuses on maximal strength in the squat, bench press, and deadlift. Bodybuilding prioritizes muscle hypertrophy through higher reps and sets. Olympic weightlifting emphasizes explosive power and technique in lifts like the snatch and clean & jerk.
For combined strength and weight loss, a balanced approach is best. A program incorporating elements of powerlifting (for strength) and bodybuilding (for hypertrophy) with proper attention to calorie intake can yield excellent results. For instance, incorporating compound movements like squats and deadlifts (powerlifting) with isolation exercises like bicep curls and tricep extensions (bodybuilding) allows for overall strength gains and targeted muscle growth.
Discover how effective strength training methods for weight gain and muscle building has transformed methods in this topic.
Training Frequency Comparison
Choosing the right training frequency depends on your recovery capacity and goals. Here’s a comparison:
| Training Frequency | Pros | Cons | Suitability for Weight Loss & Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Body | Efficient, good for beginners, frequent muscle stimulation | Can lead to overtraining if not managed carefully, requires adequate rest | Good for beginners, effective for overall strength and weight loss |
| Upper/Lower Split | Allows for more volume per muscle group, better recovery | Requires more time commitment, might be overwhelming for beginners | Suitable for intermediate and advanced lifters, excellent for building muscle and strength |
| Push/Pull/Legs | Good balance, allows for focused training on specific muscle groups | Can be time-consuming, requires careful planning | Effective for both strength and hypertrophy, good for intermediate and advanced lifters |
Designing a Weightlifting Program for Strength and Weight Loss
So, you’re ready to sculpt yourself into a superhero (or at least a slightly stronger, leaner version)? Fantastic! Designing a weightlifting program that simultaneously builds strength and melts away unwanted pounds requires a strategic approach – think of it as a meticulously crafted heist plan, but instead of robbing a bank, you’re robbing your body of excess fat.
This isn’t about some magical, overnight transformation. It’s about consistent effort, smart planning, and a healthy dose of patience. We’ll be focusing on a 12-week program that incorporates progressive overload, a principle as fundamental to strength training as oxygen is to breathing. Basically, you gradually increase the weight, reps, or sets over time to continually challenge your muscles and force them to adapt and grow stronger.
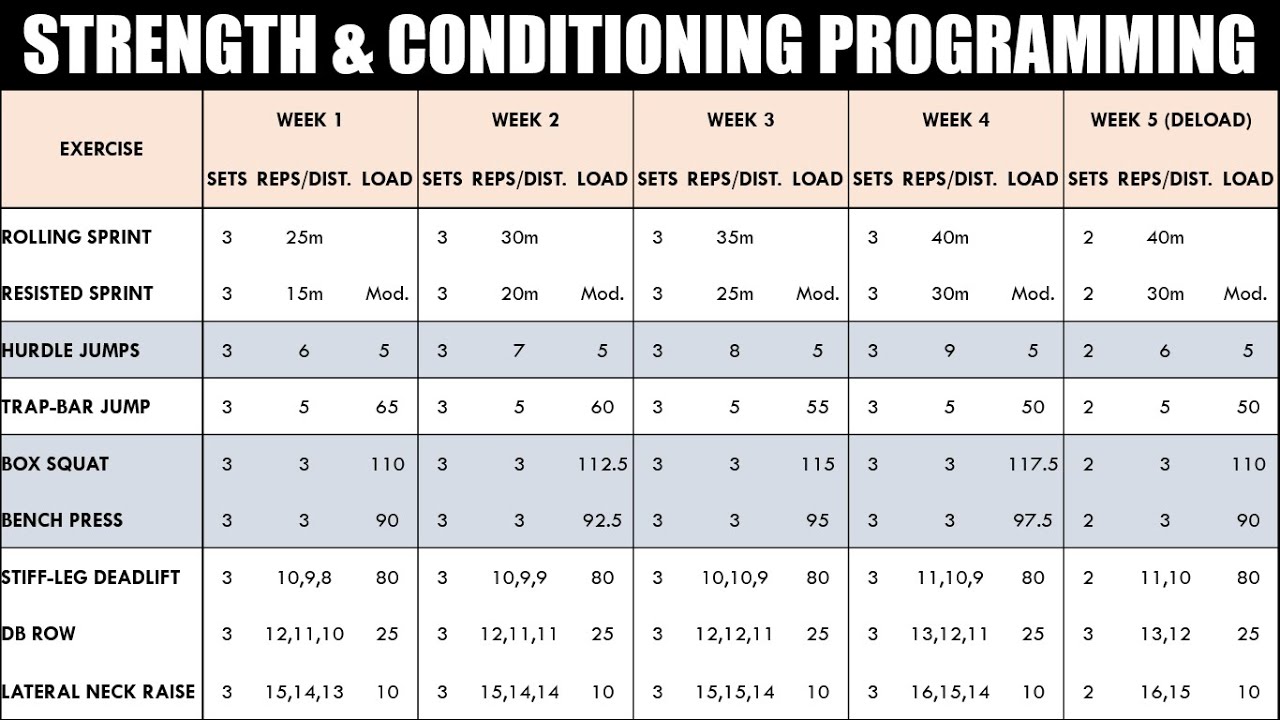
A Sample 12-Week Weightlifting Program
This program focuses on a full-body approach three times a week, allowing ample rest for muscle recovery. Remember to listen to your body; rest days are your friends, not your enemies. Adjust weights based on your individual strength levels. If something feels too heavy, lighten the load. Safety first!
| Week | Monday | Wednesday | Friday |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-4 | Squats (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Bench Press (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Bent-Over Rows (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Overhead Press (3 sets of 8-12 reps) | Rest | Squats (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Bench Press (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Bent-Over Rows (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Overhead Press (3 sets of 8-12 reps) |
| 5-8 | Squats (3 sets of 10-15 reps), Bench Press (3 sets of 10-15 reps), Bent-Over Rows (3 sets of 10-15 reps), Overhead Press (3 sets of 10-15 reps) | Rest | Squats (3 sets of 10-15 reps), Bench Press (3 sets of 10-15 reps), Bent-Over Rows (3 sets of 10-15 reps), Overhead Press (3 sets of 10-15 reps) |
| 9-12 | Squats (3 sets of 12-15 reps), Bench Press (3 sets of 12-15 reps), Bent-Over Rows (3 sets of 12-15 reps), Overhead Press (3 sets of 12-15 reps) | Rest | Squats (3 sets of 12-15 reps), Bench Press (3 sets of 12-15 reps), Bent-Over Rows (3 sets of 12-15 reps), Overhead Press (3 sets of 12-15 reps) |
Note: Progressive overload can be implemented by increasing weight, reps, or sets each week, or by changing the exercise variation. For example, you could switch from barbell squats to goblet squats for variation.
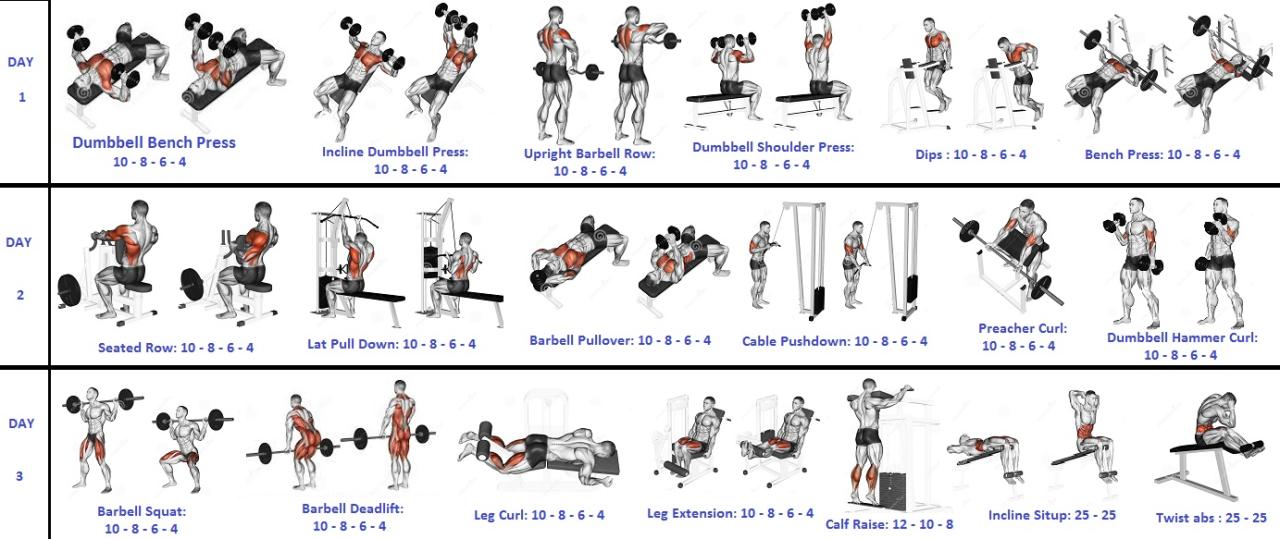
Compound Exercises: The Muscle-Building Powerhouses
Compound exercises, those that work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, are your secret weapons in this strength and weight loss battle. They’re incredibly efficient, burning more calories and building more muscle than isolation exercises.
- Squats: Works legs, glutes, core. Imagine the power of a superhero’s leap – that’s the kind of strength squats build.
- Bench Press: Targets chest, shoulders, triceps. Think of pushing a heavy car – this exercise builds that kind of pushing power.
- Bent-Over Rows: Works back, biceps, forearms. Imagine pulling a heavy rope – this is the pulling power you build.
- Overhead Press: Strengthens shoulders, triceps. Picture hoisting a heavy object overhead – that’s the power this exercise builds.
- Deadlifts: A full-body powerhouse exercise working nearly every muscle group, improving overall strength and burning a significant amount of calories.
Proper Form and Technique: Injury Prevention 101
Executing exercises with impeccable form is crucial. Poor form is a recipe for injury, which will sideline you faster than a poorly timed sneeze during a crucial moment. Start with lighter weights to master the technique before increasing the load. Consider working with a qualified trainer to learn proper form.
“Form over weight, always. It’s better to lift less weight correctly than more weight incorrectly.”
Supplementation with Isolation Exercises, Best weightlifting routine for building strength and losing weight
While compound exercises are the stars of the show, isolation exercises can help target specific muscle groups for further development and sculpting. These exercises focus on one muscle group at a time.
- Bicep Curls
- Triceps Extensions
- Lateral Raises
- Hamstring Curls
- Calf Raises
Nutrition Strategies for Optimal Results

Let’s face it: lifting weights is only half the battle. You can pump iron like a champion, but without the right fuel, your muscles will be protesting louder than a rock concert in a library. Nutrition is the unsung hero of strength building and weight loss – it’s the secret weapon that transforms your hard work into visible results.
Think of it as providing your body with the high-octane fuel it needs to perform at its peak and recover like a boss.
Adequate Protein Intake for Muscle Growth and Repair
Protein is the building block of muscle. Without sufficient protein, your muscles won’t grow, and after intense workouts, they won’t repair themselves efficiently. Imagine trying to build a house with only half the bricks – it’s not going to be a pretty sight, and it certainly won’t be structurally sound. Aim for a daily protein intake of around 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight, depending on your training intensity and goals.
Good sources include lean meats (chicken, turkey, fish), eggs, dairy products, legumes, and tofu. Consider incorporating protein shakes to supplement your diet, especially if you struggle to meet your daily protein needs through whole foods.
The Role of Carbohydrates in Providing Energy for Workouts and Overall Health
Carbohydrates are your body’s primary energy source, especially during intense workouts. Depriving yourself of carbs is like trying to run a marathon on an empty stomach – it’s not going to end well. Carbohydrates replenish glycogen stores in your muscles, fueling your lifts and preventing fatigue. Focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, oats), fruits, and vegetables.
These release energy slowly, providing sustained energy throughout the day, unlike simple carbs that lead to energy crashes. Finding the right balance is key; too many carbs can hinder weight loss, while too few can leave you feeling sluggish and impacting your performance.
Strategies for Managing Calorie Intake While Maintaining Sufficient Energy Levels
Managing calorie intake for weight loss is crucial, but it doesn’t mean starving yourself. The key is to create a calorie deficit – consuming fewer calories than you burn. This doesn’t require drastic measures; small, sustainable changes can make a big difference. Start by tracking your calorie intake using a food diary or app to understand your current consumption.
Then, gradually reduce your calorie intake by 250-500 calories per day. Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods, and avoid sugary drinks and excessive processed foods. Remember, consistency is key – small, consistent changes are far more effective than drastic, unsustainable diets. Listen to your body’s hunger cues and adjust your calorie intake accordingly.
Examine how muscular strength exercises can boost performance in your area.
Sample Meal Plan Supporting Strength Training and Weight Loss Goals
This sample meal plan provides approximately 1800-2000 calories, a moderate protein intake, and a balance of complex carbohydrates and healthy fats. Remember to adjust portion sizes based on your individual needs and activity level.
- Breakfast (400-500 calories): Oatmeal with berries and nuts, Greek yogurt with fruit and granola, or eggs with whole-wheat toast and avocado.
- Lunch (500-600 calories): Large salad with grilled chicken or fish, a whole-wheat sandwich with lean protein and vegetables, or lentil soup with a side of whole-grain bread.
- Dinner (600-700 calories): Baked salmon with roasted vegetables, chicken stir-fry with brown rice, or lean ground beef with sweet potato and broccoli.
- Snacks (200-300 calories total): A handful of almonds, Greek yogurt, fruit, or a protein shake.
Monitoring Progress and Making Adjustments
So, you’ve embarked on your weightlifting journey, fueled by dreams of sculpted muscles and a leaner physique. Fantastic! But the path to gains isn’t a straight line to the summit; it’s more like a rocky mountain trail with unexpected switchbacks. That’s where progress monitoring comes in – your trusty map and compass to navigate this exciting terrain.Tracking your progress isn’t just about vanity; it’s the key to understanding what’s working and what’s not.
Without this data, you’re essentially flying blind, potentially wasting time and effort on ineffective strategies. Think of it like this: you wouldn’t attempt a cross-country road trip without a GPS, would you? Similarly, you shouldn’t approach strength training and weight loss without diligently monitoring your progress.
Progress Tracking Methods
Regularly recording your progress provides invaluable feedback. This allows you to identify what’s working, what isn’t, and when adjustments are necessary. Consider tracking your weight weekly, body measurements (chest, waist, hips, etc.) monthly, and strength gains (how much weight you can lift for a given exercise) each workout session. A simple spreadsheet or a dedicated fitness app can make this process surprisingly easy and rewarding.
Imagine the satisfaction of seeing those numbers steadily improve! It’s a powerful visual reminder of your hard work paying off.
Identifying and Addressing Plateaus
Plateaus – those frustrating periods where progress stalls – are a completely normal part of the process. They aren’t a sign of failure, but rather an indication that your body has adapted to your current training stimulus. Don’t panic! Instead, consider these strategies:
- Increase training volume: Add more sets or reps to your exercises.
- Increase training intensity: Lift heavier weights, or reduce rest periods between sets.
- Change exercises: Introduce new exercises to challenge your muscles in different ways. If you’ve been doing bicep curls with dumbbells for months, try hammer curls or concentration curls to break the plateau.
- Adjust your nutrition: Are you consuming enough calories and protein to support your training goals? A slight adjustment to your diet might be all it takes.
- Prioritize sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for muscle recovery and growth. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Remember, finding the right approach often involves a bit of trial and error. Experiment with different combinations of these strategies until you break through the plateau.
Maintaining Motivation and Consistency
Staying motivated can be challenging, especially when progress slows. However, several strategies can help you stay the course:
- Set realistic goals: Don’t aim for unrealistic weight loss or strength gains. Set small, achievable goals that you can celebrate along the way.
- Find a workout buddy: Having a training partner can provide support, accountability, and motivation.
- Reward yourself (healthily!): Celebrate your achievements with non-food rewards, such as buying new workout gear or treating yourself to a massage.
- Track your progress visually: Charts and graphs can provide a powerful visual representation of your success.
- Remember your “why”: Reconnect with your initial reasons for starting this journey. Why did you want to get stronger and lose weight in the first place? Keeping that in mind will fuel your motivation.
Incorporating Rest and Recovery
Rest isn’t a luxury; it’s a necessity for progress. Your muscles don’t grow during your workouts; they grow during rest and recovery. Overtraining can lead to injuries, burnout, and plateaus. Make sure to incorporate rest days into your training schedule and prioritize adequate sleep. Consider active recovery methods like light cardio or stretching on your rest days to promote blood flow and reduce muscle soreness.
Listening to your body is crucial. If you feel excessively fatigued or sore, don’t hesitate to take an extra rest day. Think of it as preventative maintenance for your body’s amazing machine.
Addressing Potential Challenges and Considerations
Embarking on a weightlifting journey for strength and weight loss is a fantastic goal, but let’s be realistic – it’s not always a smooth, perfectly sculpted bicep-raising experience. Life throws curveballs, and your fitness plan needs to be agile enough to dodge them. This section tackles some common hurdles and provides strategies to help you stay on track, even when things get a little… wobbly.The path to a stronger, leaner you might be paved with good intentions, but it’s also littered with potential pitfalls.
Check what professionals state about best strength gaining exercises for building a bigger physique and its benefits for the industry.
Ignoring these could lead to frustration, injury, or even abandoning your fitness goals entirely. Let’s equip you with the knowledge and strategies to navigate these challenges successfully.
Injuries: Prevention and Management
Weightlifting, while incredibly rewarding, carries a risk of injury. Ignoring proper form, pushing yourself too hard too soon, or neglecting rest and recovery are common culprits. The key is prevention, and that starts with proper technique. Learn the correct form for each exercise, start with lighter weights, and gradually increase the weight and intensity as your strength improves.
Don’t be afraid to ask for help from a qualified trainer, especially when learning new exercises. Listen to your body – pain is not gain! If you experience sharp pain, stop immediately and seek medical attention if necessary.
Time Constraints: Making Time for Fitness
Life gets busy. Between work, family, social commitments, and the occasional zombie apocalypse (just kidding… mostly), finding time for exercise can feel like searching for a unicorn riding a bicycle. However, even short, effective workouts can yield significant results. Consider high-intensity interval training (HIIT), which maximizes calorie burn in less time. Alternatively, strategically integrate short workout sessions into your daily routine – a quick 15-minute session is better than no session at all.
Remember, consistency trumps intensity.
Expand your understanding about top strength building workout programs for rapid muscle growth with the sources we offer.
Lack of Access to Equipment: Bodyweight Training and Alternatives
Not everyone has access to a fully equipped gym. Don’t despair! Bodyweight exercises are incredibly effective for building strength and losing weight. Push-ups, squats, lunges, and planks are just a few examples. You can also explore alternatives like resistance bands, which are portable and affordable, or even utilize everyday objects like filled water bottles for added resistance.
Remember, creativity is key!
Listening to Your Body and Program Adjustment
Your body is your best guide. Pay close attention to how you feel before, during, and after your workouts. Fatigue, soreness, and minor aches are normal, but sharp pains or persistent discomfort are warning signs. Don’t hesitate to adjust your program based on your individual needs. Rest days are crucial for muscle recovery; don’t skip them! Sometimes, a lighter workout or a complete rest day is precisely what your body needs to avoid injury and continue progressing.
Common Weightlifting Injuries, Causes, and Prevention
Understanding common weightlifting injuries can help you proactively prevent them. The following table Artikels some of the most prevalent injuries, their causes, and preventative measures.
| Injury | Cause | Prevention |
|---|---|---|
| Lower Back Pain | Improper form during lifting, weak core muscles, lifting too heavy weight | Maintain proper form, strengthen core muscles, gradually increase weight |
| Knee Pain | Improper form during squats or lunges, weak leg muscles, overuse | Use proper form, strengthen leg muscles, warm up thoroughly |
| Shoulder Pain | Improper form during overhead presses, weak rotator cuff muscles, overuse | Use proper form, strengthen rotator cuff muscles, warm up thoroughly |
| Wrist Pain | Improper form during wrist curls or deadlifts, weak wrist muscles | Use proper form, strengthen wrist muscles, use wrist wraps |
Illustrative Examples of Effective Exercises
Let’s ditch the boring textbook descriptions and dive into the nitty-gritty of some seriously effective exercises. We’ll cover the big guns – the squat, bench press, deadlift, overhead press, and rows – explaining the proper form, technique, and the glorious feeling of muscle activation. Think of this as your personal, highly caffeinated, weightlifting cheat sheet.These exercises form the bedrock of any strength-building and weight-loss program.
Mastering them not only builds impressive strength but also improves posture, coordination, and overall athleticism. Remember, proper form is paramount to avoid injury and maximize results. So, let’s get those muscles firing!
Squat
The squat is the king of lower-body exercises. Imagine a powerful, graceful dip, like a superhero landing after a daring rescue. Starting with feet shoulder-width apart, toes slightly pointed outwards, lower your hips as if sitting in a chair, keeping your back straight and chest up. Your thighs should become parallel to the ground, or even lower if your flexibility allows.
The movement should originate from your hips and knees, engaging your glutes, quads, and hamstrings. Inhale as you descend, exhale forcefully as you push back up, driving through your heels. Visualize your body as a single, powerful unit, moving as one. The key is maintaining a neutral spine to avoid injury. Think of squeezing your shoulder blades together to help maintain an upright torso.
Bench Press
This classic upper-body exercise targets your chest, shoulders, and triceps. Lie on a bench with your feet flat on the floor, gripping the barbell slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Lower the bar to your chest, keeping your elbows slightly bent, and then powerfully press it back up. Imagine pushing the bar away from your chest with explosive force. Keep your back flat against the bench throughout the movement, avoiding arching.
Inhale as you lower the bar, exhale as you press it up. Visualize your chest expanding as you push the weight. Maintaining a controlled descent and a powerful ascent are key to a successful and injury-free bench press.
Deadlift
The deadlift is the ultimate full-body strength builder. Stand with your feet hip-width apart, directly over the barbell. Bend down, gripping the bar with an overhand or mixed grip (one hand overhand, one underhand), keeping your back straight and your core engaged. Lift the bar by extending your hips and knees simultaneously, keeping the bar close to your body.
Imagine lifting the bar smoothly and powerfully, as if you were pulling yourself up. The entire body should be working in sync. Inhale before you lift, exhale as you complete the lift. Visualize the bar extending upward in a straight line. Avoid rounding your back, as this is the most common cause of injury in this exercise.
Overhead Press
This exercise strengthens your shoulders, triceps, and upper back. Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a barbell at shoulder height, grip slightly wider than shoulder-width. Press the bar straight overhead, fully extending your arms. Imagine lifting the bar smoothly and powerfully, engaging your shoulder and tricep muscles. Keep your core engaged to maintain stability.
Inhale as you prepare to lift, exhale as you press the weight overhead. Visualize your arms extending straight up in a powerful, controlled motion. Avoid arching your back and maintain a stable base.
Rows
Rows are fantastic for building your back muscles, including your lats, rhomboids, and traps. Sit at a rowing machine or use dumbbells. Pull the weight towards your chest, keeping your back straight and core engaged. Squeeze your shoulder blades together at the top of the movement. Imagine pulling the weight towards your chest as if you are trying to break it in half.
Inhale as you pull the weight, exhale as you return to the starting position. Visualize your back muscles contracting and expanding with each repetition. Maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement.
Final Wrap-Up: Best Weightlifting Routine For Building Strength And Losing Weight
So, there you have it – your blueprint to a stronger, leaner you. Remember, this isn’t just about lifting weights; it’s about forging a healthier, more confident version of yourself. Embrace the challenge, celebrate the small victories (and the big ones!), and never underestimate the power of a well-placed barbell. Now go forth and conquer those weights – and maybe treat yourself to a celebratory protein shake afterwards.
You deserve it!