Best strength training workout for building lean muscle? Forget the flabby, embrace the fabulously firm! This isn’t your grandma’s aerobics class; we’re diving headfirst into the science (and the fun) of sculpting lean muscle. Prepare for a journey that’s as rewarding as it is challenging – think sculpted physique, increased strength, and maybe even the ability to finally open that stubborn pickle jar with one hand.
We’ll cover everything from beginner-friendly routines to advanced techniques, ensuring you build muscle efficiently and effectively, all while avoiding the pitfalls that can leave you feeling frustrated and sore (in a bad way).
We’ll unpack the physiological magic behind muscle growth, differentiate between simply getting stronger and actually building that coveted lean muscle mass, and even sprinkle in some delicious meal plan ideas to fuel your transformation. Get ready to ditch the excuses and unleash your inner muscle-building machine!
Introduction: Best Strength Training Workout For Building Lean Muscle
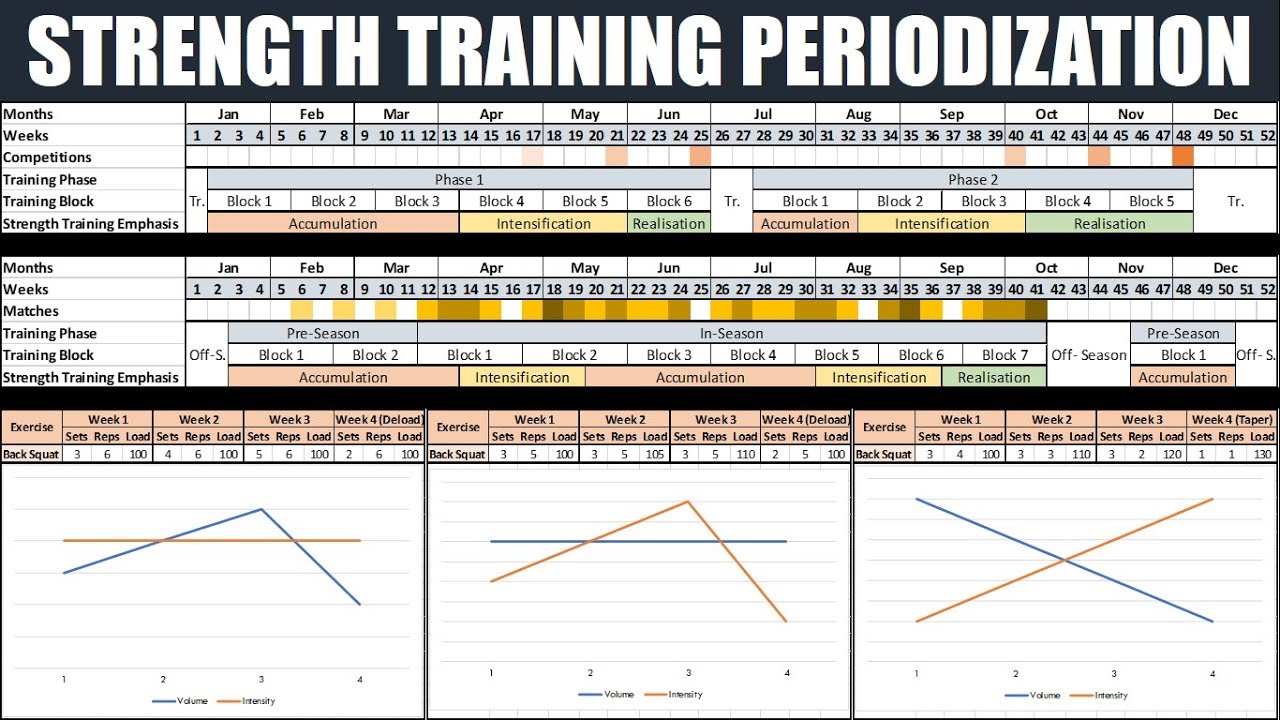
So, you want to sculpt yourself a physique worthy of a Greek god (or goddess, let’s not be sexist here)? Forget the bulky, bodybuilder look; we’re talking lean muscle – the kind that whispers strength, not shouts it. This isn’t about getting huge; it’s about gettingdefined*, powerful, and looking fantastic in that little black dress (or that perfectly tailored suit).
We’ll unravel the science behind building this coveted lean muscle, separating fact from fitness myth.Building lean muscle is a fascinating dance between your body’s incredible ability to adapt and the smart application of exercise and nutrition. It’s not just about lifting heavier weights; it’s about stimulating muscle growth at a cellular level and minimizing fat accumulation. This process involves a complex interplay of hormones, protein synthesis, and the breakdown and rebuilding of muscle tissue.
Think of it as a constant, microscopic renovation project happening within your muscles.
Muscle Hypertrophy Versus Strength Gains
Muscle hypertrophy refers to an increase in the size of your muscle fibers, leading to increased muscle mass. Imagine your muscle cells plumping up like balloons. Strength gains, on the other hand, represent an improvement in your nervous system’s ability to recruit and coordinate muscle fibers. You might not necessarily get bigger, but you get stronger, more efficient at using the muscle you already have.
Think of a finely tuned engine versus a bigger, less efficient one. Both are important for building lean muscle, but the balance will depend on your training goals. A marathon runner will prioritize strength gains for endurance, while a bodybuilder might focus more on hypertrophy for size.
Lean Muscle: Definition and Benefits
Lean muscle is simply muscle tissue with minimal fat content. It’s that aesthetically pleasing, toned look that many strive for. The benefits extend far beyond just aesthetics. Lean muscle boosts your metabolism, meaning you burn more calories even at rest. This makes weight management easier and helps to combat age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia).
Additionally, increased lean muscle mass improves strength, endurance, bone density, and overall physical function. Think of it as a long-term investment in your health and well-being – a return on investment that pays dividends for years to come. It’s not just about looking good; it’s about feeling good, too.
Fundamental Exercises for Lean Muscle Growth

Building lean muscle isn’t about magically transforming into the Hulk; it’s a gradual process requiring dedication and the right approach. Forget those crazy infomercial workouts promising overnight results – we’re focusing on sustainable, effective strength training that’ll leave you feeling strong and looking sculpted. This means prioritizing compound exercises, those that work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, for maximum bang for your buck (and minimal time spent in the gym).
We’ll dive into a beginner-friendly full-body routine, focusing on proper form to prevent injuries and maximize results. Remember, consistency is key – even small, regular efforts will yield impressive results over time. Think of it like building a house, brick by brick. You wouldn’t try to build a whole house in a day, would you? (Unless you’re a superhero, then maybe.
But even superheroes need a solid foundation.)
Want sculpted muscles that could rival a Greek goddess? The best strength training workout for building lean muscle involves compound movements and progressive overload. But ladies, if your goal is also shedding those extra pounds, check out this fantastic resource: Best strength training exercises for women to lose weight and tone up for extra tips. Then, get back to those killer squats – because lean muscle burns more calories, even when you’re chilling on the couch!
A Beginner Full-Body Strength Training Routine, Best strength training workout for building lean muscle
This routine is perfect for those just starting their fitness journey. It focuses on fundamental movements to build a solid base of strength and muscle. Remember to listen to your body and adjust the weight or reps as needed. Don’t be afraid to start light; mastering the form is far more important than lifting heavy.
| Exercise | Sets | Reps | Rest (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Squats | 3 | 8-12 | 60 |
| Push-ups | 3 | As many as possible (AMRAP) | 60 |
| Rows (using dumbbells or resistance bands) | 3 | 8-12 | 60 |
| Overhead Press (using dumbbells or resistance bands) | 3 | 8-12 | 60 |
| Plank | 3 | 30-60 seconds | 60 |
Proper Form and Execution
Proper form is crucial to avoid injuries and maximize muscle activation. Let’s break down the form for each exercise in the routine. Imagine a mirror reflecting your perfect form – that’s the image you should strive for. If you’re unsure, consider working with a trainer for a few sessions to get personalized guidance.
Squats: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, toes slightly outward. Lower your hips as if sitting in a chair, keeping your back straight and chest up. Push through your heels to return to the starting position. Avoid letting your knees cave inward.
Push-ups: Start in a plank position, hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Lower your chest towards the floor, keeping your body in a straight line. Push back up to the starting position. Modify by doing push-ups against a wall or on your knees if needed.
Rows: Sit or stand with your back straight and core engaged. Pull the weight towards your chest, squeezing your shoulder blades together. Slowly lower the weight back to the starting position.
Overhead Press: Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding dumbbells at shoulder height. Press the dumbbells straight overhead, keeping your core engaged and elbows slightly bent. Slowly lower the dumbbells back to the starting position.
Plank: Hold your body in a straight line from head to heels, supported by your forearms and toes. Engage your core and glutes to maintain proper form. Avoid sagging in the middle.
Squat Variations
The squat is a king among exercises, but it can be adapted to target different muscle groups. Here are three variations to keep things interesting and challenge your muscles from various angles.
Want sculpted muscles that’d make Michelangelo jealous? The best strength training workout for building lean muscle involves dedication and the right plan. Finding that perfect plan is key, and that’s where a killer program like the one found at best strength training program comes in handy. With the right program, you’ll be well on your way to achieving those lean, mean muscle gains – guaranteed to impress even your most critical gym buddy.
1. Standard Squat (as described above): This classic targets your quads, glutes, and hamstrings equally.
2. Front Squat: Holding the weight across your upper chest (like a goblet squat with a dumbbell or barbell across your shoulders), you emphasize your quads and core stability. It’s great for improving balance and overall strength.
3. Sumo Squat: With your feet wider than shoulder-width apart and toes pointing outward, you’ll feel this variation more in your inner thighs and glutes. It’s a fantastic way to sculpt those often-neglected areas.
Advanced Training Techniques for Lean Muscle
So, you’ve mastered the fundamentals. You’re squatting like a boss, benching like a champion, and deadlifting like…well, a deadlifting champion. But to truly sculpt that lean, mean, muscle machine, we need to delve into the slightly more advanced (and frankly, more fun) techniques. Think of this as upgrading your gym membership from basic to platinum – you get access to all the fancy equipment and personalized training plans.
This section explores advanced training strategies to supercharge your muscle growth and optimize your results. We’ll be tackling different training splits, comparing progressive overload to deload weeks, and showing you how to unleash the power of drop sets, supersets, and rest-pause sets. Prepare for muscle gains so impressive, your friends will start asking for your secret (which, of course, you’ll generously share…after they buy you a celebratory protein shake).
Training Splits: Choosing Your Muscle-Building Adventure
Choosing the right training split is like picking the perfect adventure – you want one that’s challenging but not overwhelming, and tailored to your specific goals and recovery capacity. Different splits cater to different needs and schedules. Let’s examine a few popular options:
- Upper/Lower Split: This classic split targets your upper body one day and your lower body the next. It allows for more frequent training of each muscle group, promoting greater muscle protein synthesis. However, it might not be ideal for those with very limited time or who struggle with intense training frequency.
- Push/Pull/Legs Split: This split divides exercises into pushing movements (chest, shoulders, triceps), pulling movements (back, biceps), and leg exercises. It provides excellent muscle group separation and allows for greater focus on specific muscle groups during each workout. It’s a popular choice for bodybuilders due to its effective organization.
- Full-Body Split: This involves training all muscle groups in a single workout, usually performed 2-3 times a week. It’s excellent for beginners or those short on time, but requires careful planning to avoid overtraining. The intensity needs to be managed appropriately.
The best split depends on your individual needs, recovery ability, and training goals. Experiment to find what works best for you – there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, except for the answer that involves consistently hitting the gym!
Progressive Overload vs. Deload Weeks: The Yin and Yang of Muscle Growth
Imagine your muscles as a tiny army. To get stronger, you need to constantly challenge them with progressively heavier weights or more reps. This is progressive overload – the cornerstone of muscle growth. But even the most disciplined army needs rest and recuperation. That’s where deload weeks come in.
Progressive Overload: This involves gradually increasing the weight, reps, or sets over time. It forces your muscles to adapt and grow stronger. Think of it as constantly pushing your army to conquer new territories.
Deload Weeks: These are periods of reduced training volume and intensity, allowing your body to recover and prevent overtraining. It’s like giving your army a well-deserved break before the next big battle. Without proper rest, your gains will plateau, and you risk injury.
“Without deload weeks, your body will eventually revolt, leading to overtraining, plateaus, and possible injury. Listen to your body; it’s wiser than you think.”
Incorporating Advanced Training Techniques
Now for the fun part – adding some advanced techniques to your workouts to really shake things up. These techniques can help you break through plateaus and maximize your muscle growth. But remember, proper form is paramount. Don’t sacrifice technique for intensity.
- Drop Sets: Perform a set to failure, then immediately reduce the weight and continue until failure again. Repeat this process 2-3 times. This intensifies muscle fatigue and stimulates significant growth. Imagine it like a relentless wave of attackers pushing through enemy lines.
- Supersets: Perform two exercises back-to-back with minimal rest. This increases metabolic stress and promotes significant muscle growth. Think of it as two battalions attacking simultaneously, overwhelming the enemy.
- Rest-Pause Sets: Perform a set to failure, rest for a short period (10-15 seconds), and then continue the set until failure again. Repeat this process 2-3 times. This allows you to push past your initial failure point and achieve greater muscle hypertrophy. This is like giving your army a quick breather before launching a final, devastating assault.
Remember to incorporate these advanced techniques strategically, not in every workout. Overdoing it can lead to overtraining. Start slowly, gradually increasing the frequency and intensity as you adapt.
Nutrition for Optimal Lean Muscle Growth

Fueling your body for lean muscle growth isn’t about starving yourself; it’s about strategic nourishment. Think of your muscles as high-performance engines – they need the right kind of fuel to perform optimally and build that lean, mean fighting machine you’ve been dreaming of. We’re talking about a balanced approach, not a restrictive diet. Forget the fad diets; this is about sustainable, delicious eating that supports your fitness goals.
The key to success lies in understanding the role of macronutrients – protein, carbohydrates, and fats – and how they contribute to muscle protein synthesis, recovery, and overall health. Getting the ratios right is crucial, and we’ll break down a sample plan to show you how it’s done.
Want sculpted muscles that could shame a Greek god? The best strength training workout for building lean muscle involves a smart mix of compound and isolation exercises. To really nail those gains, check out some killer moves on this site dedicated to muscular strength exercises , then get back to building that physique you’ve always dreamed of – because let’s face it, you deserve it.
Protein Intake for Muscle Protein Synthesis
Protein is the undisputed king of muscle building. It’s the building block of muscle tissue, and without sufficient protein, your gains will be severely hampered. Think of it as the raw material your body uses to construct and repair muscle fibers after intense strength training sessions. Muscle protein synthesis (MPS), the process of building new muscle protein, is heavily reliant on adequate protein intake.
A deficiency in protein will significantly reduce MPS, meaning less muscle growth. Aim for a daily protein intake of around 1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight, depending on your training intensity and individual needs. For example, a 70kg individual should consume between 112 and 154 grams of protein daily.
The Role of Carbohydrates and Healthy Fats
While protein is the star of the show, carbohydrates and healthy fats play crucial supporting roles. Carbohydrates provide the energy your body needs to power through those grueling workouts. Think of them as the fuel that keeps your engine running. Opt for complex carbohydrates like brown rice, quinoa, and sweet potatoes, which provide sustained energy release, preventing energy crashes.
So you want the best strength training workout for building lean muscle? Forget those flimsy cardio routines; real gains come from lifting heavy! If you’re a newbie, though, check out this Complete guide to weight lifting for beginners to lose weight first – it’ll save you from looking like a confused kitten in a weight room.
Then, once you’ve mastered the basics, you’ll be sculpting those lean muscles in no time! Remember, proper form is key to avoiding injury and maximizing results.
Healthy fats, found in sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are essential for hormone production, cell function, and nutrient absorption. They also contribute to satiety, keeping you feeling full and satisfied.
Sample Daily Meal Plan
This sample meal plan provides a balanced macronutrient profile, aiming for approximately 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% healthy fats. Remember to adjust portion sizes based on your individual caloric needs and activity levels. This is just a guideline, and consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist is always recommended for personalized advice.
So you want lean muscle? Forget the juice, friend; it’s all about smart strength training. Building that physique takes dedication, and a great starting point is a solid beginner program. Check out this beginner weight training program for weight loss and toning to lay your foundation. Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can level up to more advanced routines for maximum muscle gain – remember, consistency is key!
- Breakfast (400 calories, 30g protein, 40g carbs, 15g fat): Oatmeal with berries, nuts, and a scoop of protein powder.
- Lunch (500 calories, 40g protein, 50g carbs, 20g fat): Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens, avocado, and a light vinaigrette.
- Snack (200 calories, 15g protein, 20g carbs, 10g fat): Greek yogurt with a handful of almonds.
- Dinner (600 calories, 50g protein, 60g carbs, 25g fat): Baked salmon with brown rice and roasted vegetables.
- Snack (100 calories, 10g protein, 5g carbs, 5g fat): Casein protein shake before bed.
Recovery and Rest for Muscle Growth
Building lean muscle isn’t just about grueling workouts; it’s a delicate dance between pushing your limits and allowing your body the time it needs to rebuild stronger. Think of your muscles as incredibly sophisticated LEGO creations – you can build amazing things, but if you don’t give them a chance to solidify, they’ll crumble. Recovery and rest are the unsung heroes of muscle growth, and neglecting them is like trying to win a marathon on a rusty bicycle.Proper recovery isn’t just about lounging on the sofa; it’s a multifaceted process influenced by several key factors that directly impact your muscle’s ability to repair and grow.
These factors work synergistically, meaning they support and enhance each other. Ignoring one can severely hamper the effectiveness of the others.
Sleep’s Crucial Role in Muscle Repair
Adequate sleep is the cornerstone of muscle recovery. During deep sleep, your body releases growth hormone, a vital player in muscle protein synthesis – the process where your muscles repair and grow. Think of growth hormone as the construction crew that rebuilds your muscle fibers after a tough workout. Lack of sleep significantly reduces growth hormone production, leaving your muscles struggling to recover and hindering their ability to grow.
Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Consider establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine (think warm bath, calming music), and ensuring your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool to optimize your sleep quality. Imagine your muscles as a magnificent castle; without enough sleep, the builders (growth hormone) can’t finish their work, leaving the castle incomplete and vulnerable.
Hydration: The Unsung Muscle Hero
Water is not just a thirst quencher; it’s a crucial component of muscle tissue and the various metabolic processes involved in muscle recovery. Dehydration can impair muscle protein synthesis and increase muscle soreness. Proper hydration ensures efficient nutrient delivery to your muscles, helping them repair and rebuild effectively. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially before, during, and after your workouts.
A good rule of thumb is to drink half your body weight in ounces of water daily.
Stress Management: Chill Out to Build Muscle
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, a hormone that can interfere with muscle growth and even break down muscle tissue. It’s like having a demolition crew working alongside the construction crew – progress becomes incredibly slow, or even nonexistent. Managing stress through techniques like yoga, meditation, spending time in nature, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy is crucial for optimizing muscle recovery.
Finding healthy coping mechanisms for stress will allow your body to focus its energy on muscle repair and growth instead of fighting off the effects of stress.
Dreaming of sculpted muscles but gym memberships cost more than your sanity? The best strength training workout for building lean muscle often involves heavy lifting, but don’t despair! For a fantastic, budget-friendly alternative, check out this Simple home resistance band workout for strength and weight loss – it’s surprisingly effective for building lean muscle mass without breaking the bank (or your back!).
Then, gradually incorporate heavier weights to truly maximize your gains!
Workout Program Variations Based on Experience Levels
So, you’ve conquered the beginner phase and are ready to sculpt your physique like a Greek god (or goddess, let’s be inclusive!). This section Artikels how to tailor your strength training to your experience level, ensuring continuous progress and preventing those dreaded plateaus. Remember, consistency is key, but smart progression is even more crucial. We’ll move from beginner workouts to intermediate and finally, advanced programs, showing you how to adjust volume, intensity, and exercise selection along the way.
Think of it as leveling up in the gym – you wouldn’t start playing a video game on the hardest difficulty, would you?
Intermediate Workout Program
Ready to take your gains to the next level? This program builds upon the foundational exercises learned as a beginner, increasing the volume and intensity to challenge your muscles and stimulate further growth. It’s crucial to maintain good form; remember, quality over quantity! This program should be performed 3 days a week, allowing for at least one day of rest between sessions.
| Exercise | Sets | Reps | Rest (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barbell Squats | 3 | 8-12 | 90 |
| Bench Press | 3 | 8-12 | 90 |
| Bent-Over Rows | 3 | 8-12 | 90 |
| Overhead Press | 3 | 8-12 | 90 |
| Deadlifts | 1 | 5 | 120 |
| Pull-ups (or Lat Pulldowns) | 3 | As many reps as possible (AMRAP) | 60 |
Advanced Workout Program
Welcome to the big leagues! This program incorporates advanced training techniques to maximize muscle growth and strength. Expect higher volume, more intense sets, and a greater focus on progressive overload. Remember, proper form and listening to your body are paramount at this level to avoid injury. This program is designed for 4-5 days a week, with rest days strategically placed to allow for optimal recovery.
| Exercise | Sets | Reps | Rest (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barbell Squats | 5 | 5-8 | 120 |
| Bench Press | 5 | 5-8 | 120 |
| Deadlifts | 3 | 3-5 | 180 |
| Overhead Press | 4 | 6-10 | 90 |
| Pull-ups (weighted if possible) | 4 | AMRAP | 60 |
| Romanian Deadlifts | 3 | 10-15 | 60 |
| Incline Dumbbell Press | 3 | 8-12 | 90 |
| Barbell Rows | 3 | 8-12 | 90 |
Progression from Beginner to Advanced
The journey from beginner to advanced lifter is a marathon, not a sprint. The key changes involve a gradual increase in training volume (total sets and reps), intensity (weight lifted), and exercise selection. Beginners focus on mastering fundamental movements with lower volume and intensity. Intermediates build upon this foundation, increasing both volume and intensity while potentially adding more advanced exercises.
Advanced lifters push the boundaries further, employing techniques like drop sets, supersets, and higher training frequency to continuously challenge their muscles. Think of it as building a skyscraper – you start with a solid foundation, then add more floors, increasing complexity and size as you go. The progression isn’t linear; rest and recovery are equally crucial at each stage.
Addressing Common Mistakes in Strength Training
So, you’re aiming for that lean, mean, muscle-machine physique? Fantastic! But the path to sculpted perfection is paved with good intentions and, let’s be honest, a few spectacularly avoidable blunders. We’re here to help you navigate the pitfalls and emerge victorious, looking like a Greek god (or goddess, of course!).
Many aspiring muscle-builders stumble upon common mistakes that hinder progress and, in some cases, even lead to injury. Understanding these pitfalls and implementing corrective measures is crucial for achieving optimal results and maintaining a safe training regimen. Proper form, consistent effort, and adequate rest are fundamental to effective strength training. Ignoring these principles can lead to frustration, injury, and a disappointing lack of gains.
Common Strength Training Mistakes and Their Corrections
Let’s tackle some of the most frequent faux pas that plague even seasoned lifters (yes, even the pros have been there!). Avoiding these mistakes will significantly boost your progress and keep you injury-free.
- Mistake: Neglecting proper form in pursuit of heavier weights. Think you’re impressing everyone by lifting more than you can handle with proper form? Newsflash: you’re only impressing yourself with a high risk of injury.
Correction: Prioritize perfect form over weight. Start with lighter weights and focus on mastering the movement.
Gradually increase the weight only when you can maintain flawless form throughout the entire range of motion. A good rule of thumb: If it feels wrong, it probably is.
- Mistake: Ignoring the importance of compound exercises. Spending all your time curling dumbbells and neglecting the big lifts is like trying to build a house with only toothpicks.
Correction: Incorporate compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and overhead presses into your routine. These exercises work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to greater overall strength and muscle growth.
- Mistake: Training the same muscle groups every day. Your muscles need time to recover and rebuild. Think of it like this: You can’t expect a plant to grow if you never let it rest.
Correction: Implement a well-structured split routine, allowing sufficient rest between workouts for each muscle group. For example, you might train your upper body one day and your lower body the next, with rest days in between.
- Mistake: Sticking to the same workout routine forever. Your body adapts, and if you don’t challenge it, it will plateau. It’s like expecting to get stronger by only eating the same thing every day.
Correction: Periodically change your workout routine to prevent plateaus. This could involve altering the exercises, sets, reps, or rest periods.
Consider progressive overload: gradually increasing the weight, reps, or sets over time.
- Mistake: Neglecting warm-up and cool-down routines. Jumping straight into heavy lifting without preparing your body is like starting a car without warming up the engine.
Correction: Always begin your workout with a proper warm-up, including light cardio and dynamic stretching. Finish with a cool-down, incorporating static stretching to improve flexibility and reduce muscle soreness.
The Importance of Proper Form to Prevent Injuries
Proper form is paramount. It’s not just about looking good; it’s about preventing injuries and maximizing results. Think of your body as a finely tuned machine – using incorrect form is like throwing sand into the gears. It’s going to grind to a halt, and likely break down in the process.
Imagine performing a squat with rounded back: This puts immense strain on your spine, significantly increasing the risk of injury. Conversely, maintaining a neutral spine throughout the movement protects your back and allows for efficient power transfer. The same principle applies to all exercises. Invest time in learning the correct techniques. Consider working with a qualified trainer to ensure your form is impeccable before progressing to heavier weights.
Impact of Insufficient Rest and Recovery on Muscle Growth
Muscle growth doesn’t happen in the gym; it happens during rest. While you’re lifting weights, you’re creating microscopic tears in your muscle fibers. It’s during rest and recovery that your body repairs these tears, making them stronger and larger. Think of it as your muscles’ “me time” – crucial for their growth and your overall progress.
Insufficient rest leads to overtraining, characterized by fatigue, decreased performance, and increased risk of injury. It’s like trying to run a marathon without ever taking a break – you’ll eventually collapse. Prioritize sleep, nutrition, and active recovery methods such as light cardio or stretching to optimize your body’s repair processes and maximize muscle growth.
Visual Aids
Let’s ditch the blurry YouTube videos and get down to the nitty-gritty of proper form. Visualizing these exercises correctly is half the battle – the other half is, of course, actually doing them (and maybe not eating your weight in cookies afterwards). We’ll paint a picture with words, so vivid you’ll feel like you’re already in the gym, smelling the iron and the slightly-too-much-deodorant.
Bench Press Form
The bench press: a classic, a staple, a potential shoulder-wrecker if you don’t know what you’re doing. Proper form is paramount to avoid injury and maximize gains. Imagine your body as a perfectly aligned, highly efficient weight-lifting machine.
Foot Placement: Plant your feet flat on the floor, shoulder-width apart, and firmly grounded. This provides a stable base, preventing you from lifting with your legs and causing imbalance. Think of it as anchoring yourself to the earth, ready to unleash your inner Hercules (or Heracles, if you’re feeling fancy).
Back Position: Arch your lower back slightly, creating a natural curve. This keeps your spine aligned and supports your core. Don’t flatten your back against the bench – think of squeezing your shoulder blades together, creating a slight arch, not a dramatic bend. Avoid a rounded back at all costs, it’s a recipe for disaster.
Grip: Grip the bar slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Your grip should be firm but not tense. Overly tight grips can lead to unnecessary strain and fatigue. Your wrists should be straight, aligned with your forearms, and avoid any unnecessary bending. Think of a powerful, yet relaxed grip, like you’re holding a very important (and heavy) bird.
Deadlift Form
The deadlift: the king of compound exercises, a true test of strength, and a back-breaker if you’re not careful. This exercise requires a significant amount of focus on maintaining a neutral spine.
Stance and Grip: Stand with your feet hip-width apart, directly over the bar. Your shins should be close to the bar. Grip the bar with an overhand grip, slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, or use a mixed grip (one hand overhand, one underhand) for heavier weights. This provides a secure and balanced grip, allowing for a controlled lift.
Neutral Spine: Maintaining a neutral spine is crucial. This means keeping your back straight, avoiding any rounding or excessive arching. Engage your core muscles throughout the entire lift to stabilize your spine. Imagine your spine as a sturdy oak tree, unyielding and strong.
The Lift: Initiate the lift by extending your hips and knees simultaneously, keeping your back straight. The bar should move close to your body throughout the lift. Avoid jerking or swinging the weight. Pull the bar up to your hips, then stand up completely. Lower the bar by reversing the movement, maintaining a neutral spine and controlled descent.
Think of it as a smooth, powerful ascension and controlled descent, not a chaotic dance.
Squat Form
The squat: the ultimate leg builder, a testament to lower body strength, and a knee-wrecker if you don’t respect its power.
Foot Placement: Stand with your feet slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, toes pointed slightly outward (about 15-30 degrees). This provides a stable base and allows for a deeper squat. Imagine your feet forming a strong, stable triangle.
Depth: Squat down until your hips are below your knees. This is often referred to as a “parallel squat,” where your thighs are parallel to the ground. Going deeper is generally fine for experienced lifters, but prioritize proper form over depth, especially when starting. Think of it as a smooth, controlled descent to a comfortable depth.
Back Position: Maintain a neutral spine throughout the entire movement. Engage your core muscles to stabilize your spine and prevent rounding. Keep your chest up and your shoulders back. Avoid leaning too far forward or backward. Think of your back as a straight, unwavering line of strength.
Closing Notes
So there you have it – your comprehensive guide to building lean muscle through strength training. Remember, consistency is key. Don’t expect overnight miracles, but with dedication to the right exercises, nutrition, and recovery, you’ll be amazed by the transformation you achieve. Think of it as sculpting a masterpiece – it takes time, effort, and the right tools, but the final result is incredibly rewarding.
Now go forth and conquer those weights (and maybe that pickle jar too!).
