Best Weight Lifting Regimen for building serious strength and size: Forget skinny jeans and embrace the gains! This isn’t your grandma’s knitting circle; we’re diving headfirst into the world of iron, sweat, and glorious muscle growth. Prepare for a journey that’ll transform you from a wilting flower into a blossoming powerhouse. We’ll unravel the secrets to building a physique that’ll make Hercules jealous (and maybe even a little intimidated).
This guide isn’t just another workout plan; it’s your personalized blueprint to unlocking your inner beast. We’ll cover everything from mastering the art of progressive overload (think of it as a friendly competition with yourself) to the crucial role of nutrition (because abs are made in the kitchen, not just the gym). Get ready to learn how to sculpt your body into a masterpiece, one rep at a time.
Understanding Training Principles for Strength and Size

Building serious strength and size isn’t about randomly heaving weights around; it’s a science (a gloriously sweaty science, admittedly). Understanding the underlying principles is key to maximizing your gains and minimizing the risk of injury. Think of it as building a skyscraper – you need a solid foundation, not just a pile of bricks thrown together haphazardly.
Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is the cornerstone of any successful strength and size program. Simply put, it means consistently increasing the demands placed on your muscles over time. This could involve gradually increasing the weight you lift, the number of repetitions you perform, or the number of sets you complete. It’s about pushing your muscles beyond their comfort zone, forcing them to adapt and grow stronger and bigger.
Imagine a weightlifter who can bench press 100kg for 5 reps. To progress, they might increase the weight to 102.5kg, maintain the reps, add a set, or even try a different variation of the bench press to challenge their muscles in a new way. Stagnation is the enemy of progress; constant progression is the key to unlocking your full potential.
Rest and Recovery
Think of your muscles as incredibly resilient sponges – they soak up the stress of training, but they need time to squeeze out the lactic acid and rebuild themselves bigger and stronger. Adequate rest and recovery aren’t optional extras; they’re essential for muscle growth and preventing overtraining. Sleep is crucial, aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Proper nutrition plays a huge role (more on that later!), and incorporating active recovery methods like light cardio or stretching can also help. Ignoring rest is like trying to build a skyscraper without breaks – you’ll eventually collapse under the pressure.
Nutrition’s Role in Muscle Growth and Strength Gains
Your muscles are essentially protein factories. To build them up, you need to supply the raw materials – protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Protein provides the building blocks for muscle tissue, carbohydrates provide the energy for your workouts, and healthy fats support hormone production and overall health. Think of it like this: you can’t build a skyscraper out of cotton candy.
You need sufficient calories to support your training volume and a diet rich in protein to fuel muscle growth. A general guideline is to consume 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily. Remember, consistency is key!
Periodization in Weightlifting Programs
Periodization is essentially the strategic planning of your training over time. Instead of constantly training at maximum intensity, you vary the intensity, volume, and type of training throughout different phases. This helps prevent overtraining, allows for periods of focused strength or hypertrophy development, and helps you peak for specific events or goals. It’s like training for a marathon – you don’t run a marathon every day.
You build up your endurance gradually. A typical periodization plan might involve a hypertrophy phase (high volume, moderate intensity), followed by a strength phase (low volume, high intensity), and then a peaking phase (tapering volume and intensity).
Comparison of Training Splits
Choosing the right training split depends on your individual goals, experience level, and recovery capacity. Here’s a comparison of popular splits:
| Split Type | Training Frequency | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper/Lower | 4-6 days/week | Allows for sufficient recovery, good for beginners and intermediates | Can be less time-efficient than other splits for advanced lifters |
| Push/Pull/Legs | 3-6 days/week | Effective for balanced muscle development, allows for more frequent training of each muscle group | Requires careful planning to avoid overtraining |
| Full Body | 3-4 days/week | Time-efficient, good for beginners, promotes overall strength | Can be very demanding on recovery, may limit training volume for each muscle group |
| Bro Split | 6 days/week | Allows for high volume training of each muscle group | High risk of overtraining, may not be suitable for all individuals |
Exercise Selection for Optimal Results
Choosing the right exercises is crucial for building serious strength and size. Think of it like this: you wouldn’t try to build a skyscraper with only toothpicks, would you? Similarly, relying on a limited range of exercises will leave your gains stunted. We need a strategic blend of compound movements – the heavy hitters – and isolation exercises – the fine-tuners – to sculpt a truly impressive physique.
Compound Exercises for Overall Strength
Compound exercises work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to greater overall strength gains and calorie burn. These are your foundation, the bedrock upon which your gains are built. Neglecting them is like trying to bake a cake without flour – it’s not going to happen.
- Squats: The king of leg exercises, targeting quads, hamstrings, and glutes. Think of it as a full-body power surge.
- Bench Press: The undisputed champion of chest development, also engaging shoulders and triceps. It’s the ultimate upper body challenge.
- Deadlifts: The ultimate full-body exercise, working nearly every muscle group from head to toe. This is where serious strength is forged.
- Overhead Press: A fantastic shoulder builder, also engaging triceps and upper back. Think of it as the ultimate shoulder sculptor.
- Barbell Rows: A powerful back exercise, crucial for posture and overall strength. A strong back is a happy back.
Isolation Exercises for Targeted Muscle Growth
Once you’ve laid the foundation with compound exercises, isolation exercises allow you to target specific muscle groups for further growth and definition. These are your precision instruments, refining the masterpiece you’ve started.
Browse the implementation of Weight training program for building strength and improving overall fitness in real-world situations to understand its applications.
- Bicep Curls: For those glorious biceps. Think bulging arms.
- Triceps Extensions: To sculpt those horseshoe triceps. The ultimate arm finisher.
- Lateral Raises: For those broad, impressive shoulders. The key to shoulder definition.
- Hamstring Curls: To target those often-neglected hamstrings. Balanced leg development is key.
- Calf Raises: For those powerful calves. Don’t forget your lower legs!
Proper Form and Technique, Best weight lifting regimen for building serious strength and size
Proper form is paramount. Lifting heavy with bad form is a recipe for injury and suboptimal results. Think of it as driving a Ferrari with your eyes closed – it’s not going to end well. Here’s a visual representation of proper form for three key compound lifts:
Bench Press: Imagine a straight line from your head, down your shoulders, and through your hips to your heels. Your feet should be flat on the floor. Lie flat on the bench with your feet planted firmly on the ground. Grip the bar slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Lower the bar to your chest, touching lightly, then push it back up explosively.
Control the descent.
Squat: Imagine a straight line from your head, through your shoulders, hips, and knees to your ankles. Your feet should be shoulder-width apart, with your toes slightly pointed outwards. Maintain a straight back throughout the movement. Lower your hips until your thighs are parallel to the ground, keeping your chest up and your weight in your heels.
Push back up to the starting position.
Deadlift: Imagine a straight line from your head to your heels. Your feet should be hip-width apart. Keep your back straight and your core engaged. Bend down and grip the bar with an overhand grip, slightly wider than shoulder-width. Lift the bar by extending your hips and knees simultaneously.
Keep your back straight and the bar close to your body. Lower the bar slowly, maintaining a straight back.
Sample Workout Routine
This routine incorporates both compound and isolation exercises. Remember to adjust the weight to suit your strength level.
- Day 1: Legs & Shoulders
- Squats: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Leg Press: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
- Overhead Press: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Lateral Raises: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Day 2: Chest & Back
- Bench Press: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Incline Dumbbell Press: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
- Barbell Rows: 3 sets of 8-12 reps
- Pull-ups (or Lat Pulldowns): 3 sets to failure
- Day 3: Arms & Calves
- Bicep Curls: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
- Hammer Curls: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
- Triceps Extensions: 3 sets of 10-15 reps
- Overhead Triceps Extensions: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
- Calf Raises: 3 sets of 15-20 reps
Programming Considerations for Strength and Size Gains: Best Weight Lifting Regimen For Building Serious Strength And Size
So, you’ve picked your exercises, you understand the principles – now it’s time to get strategic. Building serious strength and size isn’t just about lifting heavy things; it’s about orchestrating a symphony of sets, reps, and rest, all while avoiding burnout and injury. Think of your training program as a meticulously crafted masterpiece, not a haphazard scribble on a napkin.
Proper programming is the key to unlocking your genetic potential. It’s the difference between steady, consistent progress and hitting a plateau faster than you can say “protein shake.” This section will dive into the nuances of programming for maximizing both strength and hypertrophy (muscle growth).
Obtain access to best strength training program to private resources that are additional.
Rep Ranges for Strength and Hypertrophy
Different rep ranges elicit different physiological responses. For maximal strength gains, lower rep ranges (1-5 reps) are king. These heavy lifts recruit the maximum number of muscle fibers, leading to significant neurological adaptations. Think of it like training your nervous system to fire all cylinders at once. On the other hand, higher rep ranges (8-12 reps or even higher, up to 20+), are more effective for muscle hypertrophy.
This higher rep range leads to increased muscle damage and subsequent growth. It’s like giving your muscles a serious workout, forcing them to adapt and grow bigger and stronger to handle the increased demand. Somewhere in the middle (6-8 reps) sits a happy medium, offering a good balance between strength and size gains.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of Effective weight lifting program for muscle growth and strength.
Benefits of Varying Training Intensity and Volume
Think of your training like a rollercoaster. Constant intensity and volume will leave you exhausted and prone to injury. Varying these elements keeps your body guessing, preventing adaptation and promoting continuous progress. Increasing the intensity (weight lifted) challenges your nervous system and stimulates strength gains, while increasing the volume (sets and reps) increases muscle hypertrophy. Cycling between high-intensity, lower-volume phases and lower-intensity, higher-volume phases is a common and effective strategy.
Imagine a powerlifter alternating between heavy lifting days and higher-rep accessory work days; that’s precisely the principle at play here.
Learn about more about the process of Advanced weight lifting exercises for experienced lifters to build strength in the field.
Tracking Progress and Program Adjustment
Tracking your progress is as crucial as the training itself. This isn’t about obsessive record-keeping; it’s about objectively assessing your performance. Are you getting stronger? Are your muscles growing? If not, adjustments are necessary.
Consider using a training journal to record your sets, reps, weight, and perceived exertion. Don’t be afraid to tweak your program based on your progress. If you’re stuck, you might need to adjust your exercise selection, rep ranges, sets, rest periods, or even your overall training split. This is where flexibility and observation become your best tools.
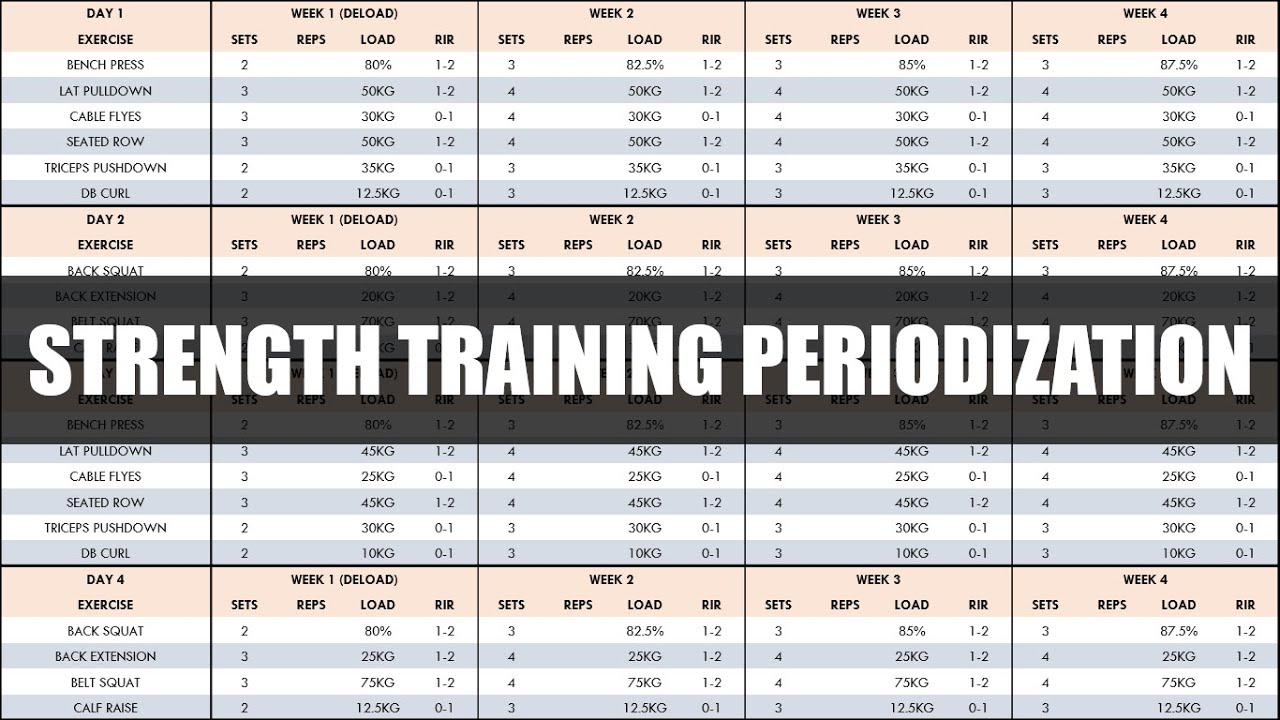
Sample 12-Week Training Program
This program gradually increases intensity and volume over 12 weeks, incorporating deload weeks to prevent overtraining. Remember to choose exercises appropriate for your skill level and always prioritize proper form.
Each week follows a similar structure, progressing in weight and/or reps over the 4-week blocks. The example below focuses on a full-body split for simplicity, but it could be easily adapted to upper/lower or push/pull/legs splits.
- Week 1-4: Focus on mastering form and building a solid base. Moderate weight, 8-12 reps per set.
- Week 5-8: Increase the weight slightly, aiming for 6-8 reps per set. Increase the total volume slightly as well.
- Week 9: Deload week. Reduce weight and volume significantly. Focus on active recovery.
- Week 10-12: Push for higher intensity, aiming for 3-5 reps per set. Maintain moderate volume.
A typical weekly plan within each 4-week block might look like this (adjust based on your chosen exercises):
- Monday: Full body workout focusing on compound movements (squats, bench press, deadlifts, overhead press, rows).
- Tuesday: Rest or Active Recovery (light cardio, stretching).
- Wednesday: Full body workout focusing on accessory exercises (bicep curls, triceps extensions, calf raises).
- Thursday: Rest or Active Recovery.
- Friday: Full body workout focusing on compound movements.
- Saturday & Sunday: Rest.
Implementing Deload Weeks
Deload weeks are your training program’s best friend. They prevent overtraining, allowing your body to recover and rebuild. They’re not “rest weeks”—you’ll still train, but at a significantly reduced intensity and volume. Think of it as giving your muscles a breather, allowing them to repair the micro-tears caused by intense training, which in turn leads to better strength and size gains in the long run.
A common approach is to reduce the weight by 40-50% and the volume by 50-60%. This allows for recovery without completely losing your hard-earned gains.
Nutrition and Supplementation Strategies
Fueling your body like a finely-tuned sports car is crucial for building serious strength and size. Forget chugging sugary drinks and surviving on ramen – we’re talking about a strategic approach to nutrition that will supercharge your gains. This isn’t about deprivation; it’s about optimizing your intake to maximize muscle growth and recovery.
Macronutrient Requirements for Muscle Growth and Strength Gains
The foundation of any successful weightlifting nutrition plan rests on the three macronutrients: protein, carbohydrates, and fats. Protein is the undisputed king for muscle building, providing the amino acids necessary for muscle repair and growth. Carbohydrates are your body’s primary energy source, fueling your intense workouts and preventing muscle breakdown. Fats, often unfairly maligned, are essential for hormone production and overall health, contributing to optimal function.
The ideal ratio varies depending on individual factors like training intensity and body composition, but a common guideline is 40% carbohydrates, 30% protein, and 30% fats. Remember, this is a guideline, not a strict rule. Experiment to find what works best for you.
Practical Tips for Meal Timing and Preparation
Meal timing is less about strict adherence to schedules and more about consistent nutrient intake throughout the day. Aim for roughly 4-6 meals, spaced approximately 3-4 hours apart, to keep your energy levels stable and your muscles constantly fed. Preparation is key to staying on track. Batch cooking on weekends, utilizing meal prepping techniques, and keeping healthy snacks readily available will save you time and keep you from making impulsive, less-than-optimal food choices.
Think of it as investing in your gains – a small amount of time spent now will yield significant results in the long run.
Sample Meal Plan
Here’s a sample meal plan, but remember to adjust portion sizes based on your individual caloric needs and activity level.
- Meal 1 (Breakfast): Oatmeal (50g carbs) with berries (10g carbs, 2g protein) and a scoop of whey protein (30g protein) – Macronutrient Breakdown: 60g carbs, 32g protein, 5g fat
- Meal 2 (Mid-morning snack): Greek yogurt (20g protein) with almonds (10g fat) – Macronutrient Breakdown: 5g carbs, 20g protein, 15g fat
- Meal 3 (Lunch): Chicken breast (40g protein) with brown rice (50g carbs) and broccoli (5g carbs, 5g protein) – Macronutrient Breakdown: 55g carbs, 45g protein, 5g fat
- Meal 4 (Pre-workout snack): Banana (25g carbs) with peanut butter (7g protein, 15g fat) – Macronutrient Breakdown: 25g carbs, 7g protein, 15g fat
- Meal 5 (Post-workout shake): Whey protein shake (30g protein) with creatine (optional) – Macronutrient Breakdown: 5g carbs, 30g protein, 2g fat
- Meal 6 (Dinner): Salmon (30g protein, 20g fat) with sweet potato (30g carbs) and asparagus (5g carbs, 3g protein) – Macronutrient Breakdown: 35g carbs, 33g protein, 25g fat
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Common Supplements
Supplements can be helpful, but they shouldn’t replace a solid diet and training program. Think of them as supporting players, not the main stars. Creatine, for example, can increase strength and power output, but it can also cause water retention. Whey protein is a convenient and efficient way to increase protein intake, but some individuals might experience digestive discomfort.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Comparison of Protein Sources
| Protein Source | Protein Content (per 100g) | Digestibility | Cost | Potential Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whey Protein | 70-80g | High | Moderate | Bloating, gas (in some individuals) |
| Casein Protein | 70-80g | Moderate (slower digestion) | Moderate | Less likely to cause bloating than whey |
| Soy Protein | 50-70g | Moderate | Low | Potential for allergic reactions in some individuals |
| Chicken Breast | 30g | High | Moderate | Rarely causes side effects |
Addressing Potential Challenges and Plateaus
Hitting a plateau in your strength and size gains? Don’t despair, you’re not alone! Many lifters experience periods where progress seems to stall, leaving them feeling frustrated and questioning their methods. This section will explore the common culprits behind these frustrating roadblocks and provide strategies to help you smash through them and continue your journey towards muscle-bound magnificence.The reality is, progress isn’t always linear.
It’s more like a staircase with occasional plateaus – periods of seemingly stagnant growth – before you ascend to new heights. Understanding the reasons behind these plateaus is the first step to overcoming them.
Causes of Training Plateaus
Several factors contribute to plateaus. These range from training-related issues (like inadequate stimulus or poor program design) to lifestyle factors (like insufficient sleep or nutrition). Ignoring these factors can lead to frustration and even injury. Let’s delve into some key areas. Firstly, inadequate training stimulus is a major player.
If your workouts aren’t challenging enough, your body won’t adapt and grow. Secondly, poor program design is another common culprit. A program that lacks variety or doesn’t progressively overload your muscles will eventually lead to stagnation. Finally, neglecting the basics, such as sufficient sleep, proper nutrition, and stress management, can severely hinder your progress.
Strategies for Overcoming Training Plateaus
Once you’ve identified the potential reasons for your plateau, it’s time to take action. A multifaceted approach is often the most effective. Consider implementing a deload week, which involves significantly reducing training volume and intensity to allow your body to recover. This can help alleviate fatigue and prevent overtraining. Another effective strategy is to change your training split, for example, shifting from an upper/lower split to a push/pull/legs split, to stimulate different muscle groups in novel ways.
Don’t forget to incorporate progressive overload; consistently increase the weight, reps, or sets over time to continuously challenge your muscles. Finally, consider consulting a qualified strength and conditioning coach for personalized guidance and program adjustments. They can assess your training, identify weaknesses, and tailor a plan to help you break through your plateau.
The Importance of Listening to Your Body and Adjusting the Program
Your body is a complex machine, and it’s crucial to listen to its signals. Ignoring pain or persistent fatigue can lead to injuries and setbacks. Regular self-assessment is key; pay attention to your energy levels, sleep quality, and overall mood. If you notice any significant changes, don’t hesitate to adjust your training program. This might involve reducing the volume or intensity of your workouts, incorporating rest days, or even taking a complete break from training for a short period.
Remember, progress is a marathon, not a sprint, and sometimes taking a step back can propel you forward.
Managing Injuries and Preventing Overtraining
Overtraining is a serious issue that can lead to burnout, injury, and even hormonal imbalances. Symptoms can include persistent fatigue, decreased performance, mood swings, and sleep disturbances. Prevention is key. Prioritize adequate rest and recovery, and listen to your body’s signals. Ensure your training program is balanced and progressively overloaded.
Avoid training to complete exhaustion every session. Incorporate active recovery methods such as light cardio or stretching to improve blood flow and reduce muscle soreness. Manage stress through techniques like meditation or yoga. If you suspect you are overtrained, consult a healthcare professional.
Common Weightlifting Injuries and Their Preventative Measures
Understanding common weightlifting injuries and their prevention is crucial for long-term success. Ignoring proper form and neglecting recovery can lead to serious problems. Proper warm-up before each workout is essential, and remember to cool down afterward. Always maintain good form during exercises, focusing on controlled movements and avoiding jerky motions. Gradual progression is vital – avoid increasing weight or intensity too rapidly.
- Lower Back Pain: Preventative measures include maintaining proper form during squats and deadlifts, strengthening core muscles, and avoiding excessive weight.
- Knee Pain: Proper form during squats and lunges, strengthening quadriceps and hamstrings, and avoiding valgus collapse (knees caving inward) are crucial preventative steps.
- Shoulder Injuries (Rotator Cuff Tears, etc.): Maintaining proper form during overhead presses and bench presses, strengthening rotator cuff muscles, and avoiding excessive weight are essential.
- Wrist Pain: Using proper wrist straps during exercises like deadlifts and rows, strengthening wrist extensors and flexors, and avoiding excessive weight can prevent injuries.
- Elbow Pain (Golfer’s or Tennis Elbow): Maintaining proper form during bicep curls and triceps extensions, stretching forearms regularly, and avoiding excessive weight are important.
Closing Summary
So there you have it – your comprehensive guide to conquering the weight room and achieving the physique of your dreams. Remember, consistency is key. Don’t expect miracles overnight; building serious strength and size takes dedication, smart training, and a healthy dose of self-belief. Embrace the challenge, celebrate the small victories, and get ready to unleash your inner titan.
Now go forth and lift!
