Effective Weight Lifting Routines for Building Muscle Mass Quickly: Forget the slow, agonizing crawl towards a bigger physique! This isn’t your grandpappy’s weightlifting guide; we’re talking about strategically sculpted muscle gains, achieved with the efficiency of a Swiss watch (but with way more grunting). Prepare to unleash your inner Hulk – or at least, a significantly more muscular version of yourself.
We’ll dissect the science of muscle growth, craft a personalized plan to obliterate your plateaus, and arm you with the nutritional know-how to fuel your transformation. Get ready to lift heavier, recover faster, and finally achieve the physique you’ve always dreamed of.
This guide will walk you through the essential principles of muscle growth, from understanding the hormonal symphony orchestrating your gains to mastering the art of progressive overload. We’ll design customized weightlifting programs tailored to different experience levels, incorporating high-volume and low-volume training methods for maximum impact. We’ll delve into the nuances of rep ranges and set numbers, explore the best compound and isolation exercises, and provide you with a comprehensive nutritional strategy to fuel your muscles and optimize recovery.
Think of it as your personal muscle-building playbook, complete with advanced techniques to supercharge your results and avoid common pitfalls.
Understanding Muscle Growth Principles

Building muscle isn’t just about lifting heavy things; it’s a complex biological dance orchestrated by your body’s internal chemistry and your commitment to consistent training. Think of your muscles as incredibly adaptable sculptors, constantly reshaping themselves in response to the demands you place upon them. Let’s delve into the fascinating science behind this transformation.
Muscle hypertrophy, the glorious increase in muscle size, is primarily driven by two key processes: muscle protein synthesis (MPS) and muscle protein breakdown (MPB). Imagine MPS as the construction crew, diligently building new muscle proteins, and MPB as the demolition crew, breaking down existing proteins. For muscle growth to occur, the construction crew needs to be working overtime, significantly outpacing the demolition crew.
This positive protein balance is the foundation of muscle growth.
The Role of Hormones in Muscle Growth
Hormones act as the master conductors of this biological symphony, influencing both MPS and MPB. Testosterone, often dubbed the “king” of muscle-building hormones, plays a crucial role in stimulating MPS and increasing the rate of muscle protein synthesis. It’s like adding extra workers to the construction crew, boosting the efficiency of muscle building. Growth hormone (GH) also contributes significantly by promoting protein synthesis and reducing MPB.
Think of GH as the project manager, ensuring the construction crew has all the necessary resources and minimizing disruptions. Sufficient sleep and a healthy diet are crucial for optimal hormone production – neglecting these is like leaving the project manager and construction crew short-handed.
Progressive Overload: The Key to Continuous Growth
Progressive overload is the cornerstone of any effective weightlifting program. It simply means consistently increasing the demands placed on your muscles over time. This could involve gradually increasing the weight you lift, the number of repetitions you perform, or the number of sets you complete. Without progressive overload, your muscles adapt to the existing stimulus and plateau. Imagine a weightlifter who consistently lifts the same weight for months; eventually, their muscles will adapt, and no further growth will occur.
Progressive overload ensures your muscles are continuously challenged, forcing them to adapt and grow stronger and larger. This could look like adding 2.5 lbs to your bench press every week, or increasing your reps from 8 to 10 over the course of a month.
Muscle Protein Synthesis and Breakdown: The Building and Demolishing Crew
Muscle protein synthesis (MPS) is the process by which your body builds new muscle proteins. Think of this as the construction crew adding new bricks to a wall. The rate of MPS is influenced by factors such as nutrition, training, and hormonal levels. Muscle protein breakdown (MPB) is the counterpoint; it’s the process by which your body breaks down existing muscle proteins.
This is the demolition crew removing old, damaged materials. The balance between MPS and MPB determines whether your muscles grow or shrink. A positive balance, where MPS significantly exceeds MPB, leads to muscle hypertrophy. A negative balance, where MPB dominates, leads to muscle loss. This balance is heavily influenced by your training intensity, nutrition (particularly protein intake), and rest.
Consuming enough protein, particularly after workouts, is crucial for maximizing MPS and minimizing MPB. Imagine a construction crew without enough bricks – they can’t build efficiently!
Designing a Weightlifting Program for Muscle Mass

So, you’re ready to sculpt yourself into a masterpiece of muscle? Fantastic! But before you start chucking around weights like a weightlifting Viking, a well-structured plan is key. Think of it as an architectural blueprint for your body’s new, more muscular temple. Without a plan, you risk injury and suboptimal gains – basically, a lot of wasted effort and maybe some bruised egos.
Designing a successful weightlifting program requires a blend of science and sensible planning. We’ll cover a sample 12-week program for beginners, explore high-volume versus low-volume training, dissect workout splits, and delve into the crucial world of rep ranges and sets. Get ready to unleash your inner muscle-building machine!
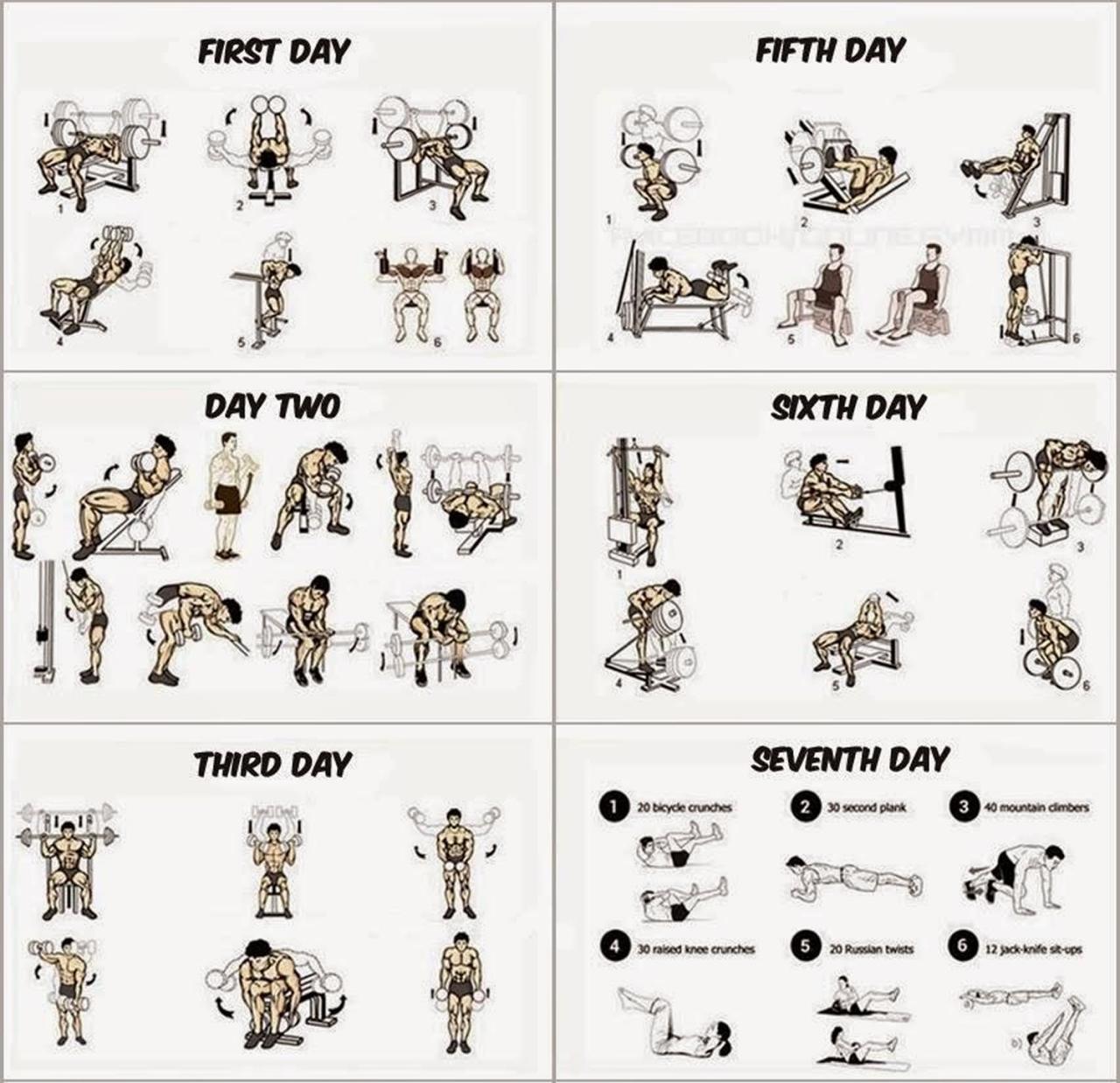
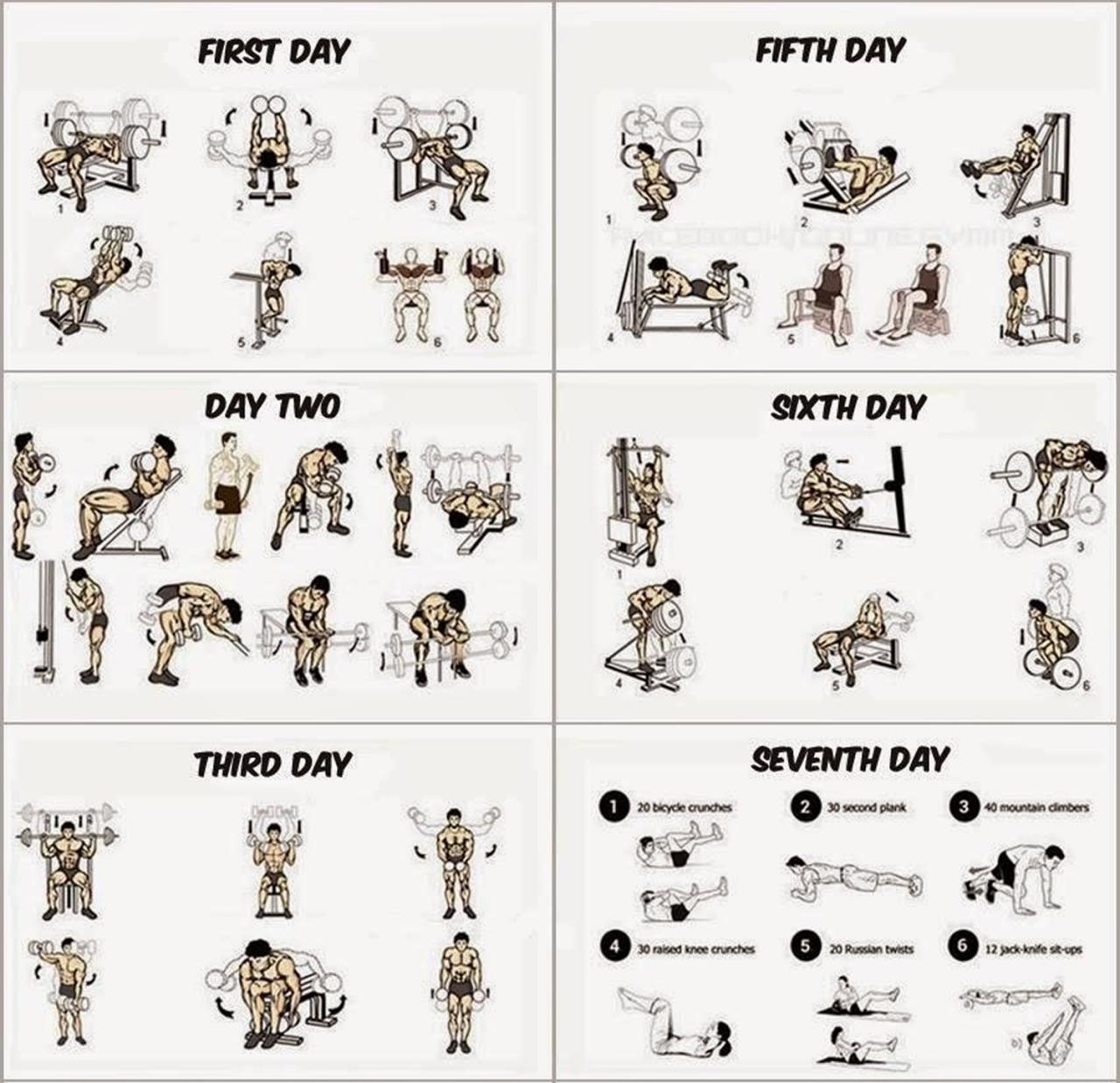
A 12-Week Beginner Weightlifting Program
This program focuses on compound exercises – movements that work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, maximizing efficiency and growth. Remember, proper form is paramount. If you’re unsure about any exercise, consult a qualified trainer.
This program assumes 3 workouts per week, with rest days in between. Adjust weights to maintain good form throughout each set. Listen to your body and don’t hesitate to take extra rest days if needed. Progress gradually – adding weight, reps, or sets as you get stronger.
| Day | Workout | Exercises (3 sets of 8-12 reps unless otherwise noted) |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Upper Body | Bench Press, Overhead Press, Bent-Over Rows, Bicep Curls, Triceps Extensions |
| Wednesday | Lower Body | Squats, Deadlifts (1-3 sets of 5 reps), Romanian Deadlifts, Leg Press, Calf Raises |
| Friday | Full Body | Pull-ups (or Lat Pulldowns), Push-ups, Lunges, Plank (3 sets, 30-60 seconds hold) |
High-Volume vs. Low-Volume Training
High-volume training involves many sets and reps, leading to significant muscle fatigue and growth. Low-volume training, conversely, prioritizes fewer sets and reps with heavier weight, emphasizing strength gains which indirectly stimulate muscle growth. Think of it like this: high-volume is a marathon, low-volume is a series of intense sprints.
Both methods are effective; the best approach depends on individual factors like experience, recovery ability, and training goals. Experiment to find what works best for you. A balanced approach, incorporating both methods periodically, can be particularly beneficial.
Workout Split Routines: Upper/Lower
The Upper/Lower split divides workouts into upper body and lower body days. This allows for more focused training and adequate recovery for each muscle group. It’s a popular choice for its simplicity and effectiveness.
This split prevents overtraining by giving each muscle group sufficient rest before being worked again. For example, after an intense upper body workout, your lower body can be trained, allowing your upper body to recover.
Rep Ranges and Set Numbers
The number of sets and reps you perform influences muscle growth. Generally, higher reps (12-15) with moderate weight build muscle endurance and hypertrophy (muscle growth). Lower reps (1-5) with heavier weight build strength, which also contributes to muscle growth.
A good starting point is 3 sets of 8-12 reps for most muscle groups. You can adjust this based on your progress and individual needs. For example, you might use a higher rep range for smaller muscle groups like biceps and triceps.
Warm-up and Cool-down Routines
A proper warm-up prepares your body for the workout, preventing injury and improving performance. A dynamic warm-up, involving movements like arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists, is ideal.
A cool-down helps your body recover and reduces muscle soreness. This could include light cardio, like walking on a treadmill, and static stretching, holding each stretch for 20-30 seconds. Think of it as giving your muscles a gentle massage after a hard day’s work.
Choosing the Right Exercises
So, you’re ready to sculpt yourself into a magnificent specimen of human strength? Excellent! But before you start flinging weights around like a caffeinated octopus, let’s talk strategy. Choosing the right exercises is the cornerstone of a successful muscle-building program. Think of it as choosing the right tools for a master carpenter – a rusty spoon won’t build a cathedral, and neither will haphazard exercise selection build a body worthy of admiration (and maybe a few envious glances).The most effective exercises for packing on muscle mass are compound movements.
These are exercises that work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to greater overall muscle growth and calorie burn. They’re the workhorses of your weightlifting regimen, the heavy lifters of the muscle-building world. Isolation exercises have their place, but the foundation is always compound movements.
Effective Compound Exercises, Effective weight lifting routines for building muscle mass quickly
Compound exercises are your bread and butter. They’re the big guns that will trigger significant muscle growth. Think of them as the all-you-can-eat buffet of muscle stimulation. We’re talking about exercises that recruit multiple muscle groups to perform a single movement. Mastering these will lay the foundation for a truly impressive physique.
Examples include the squat, deadlift, bench press, overhead press, and rows. These are the king and queen of muscle building, and you’ll want to incorporate them into your routine.
Variations of Compound Exercises
There’s more to compound exercises than meets the eye (or muscle). Each exercise has numerous variations, allowing you to target specific muscle fibers and prevent plateaus. For example, the bench press has countless variations: incline bench press (targets upper chest), decline bench press (targets lower chest), close-grip bench press (targets triceps), and wide-grip bench press (targets chest width). Similarly, squats can be performed with a barbell, dumbbells, or even just your bodyweight, each offering a slightly different emphasis.
Experimenting with variations keeps your muscles guessing and prevents adaptation.
Proper Form for Key Compound Exercises
Proper form is paramount, not just for maximizing muscle growth, but also for preventing injuries. Think of it as the fine print in your muscle-building contract – ignoring it will result in penalties (injuries). Let’s look at the squat: stand with feet shoulder-width apart, barbell across your upper back, chest up, core engaged. Descend until your thighs are parallel to the ground, maintaining a straight back and pushing through your heels.
For the bench press: lie on the bench with feet flat on the floor, grip the bar slightly wider than shoulder-width, lower the bar to your chest, and push back up. The deadlift requires a more detailed explanation and professional guidance to master proper form safely. Always prioritize proper form over weight lifted.
The Role of Isolation Exercises
While compound exercises are the stars of the show, isolation exercises play a crucial supporting role. These exercises focus on a single muscle group, allowing for targeted hypertrophy and addressing any muscle imbalances. Bicep curls, triceps extensions, and calf raises are examples of isolation exercises. They are used to fine-tune muscle development and address weaknesses. Think of them as the finishing touches on a masterpiece.
They don’t build the whole structure, but they add the detail and definition that makes it truly exceptional.
Exercise Table
| Exercise | Target Muscle Group(s) | Variations |
|---|---|---|
| Squat | Quads, Glutes, Hamstrings | Barbell Squat, Goblet Squat, Front Squat, Lunges |
| Bench Press | Chest, Triceps, Shoulders | Incline Bench Press, Decline Bench Press, Close-Grip Bench Press, Dumbbell Bench Press |
| Deadlift | Hamstrings, Glutes, Back, Core | Conventional Deadlift, Sumo Deadlift, Romanian Deadlift |
| Overhead Press | Shoulders, Triceps | Barbell Overhead Press, Dumbbell Overhead Press, Arnold Press |
Nutrition and Recovery for Muscle Growth
Fueling your body for muscle growth isn’t just about lifting heavy; it’s about providing your muscles with the building blocks and the energy they need to repair and grow bigger and stronger. Think of it like this: you wouldn’t expect a skyscraper to be built without enough bricks and cement, would you? The same principle applies to your muscles.
Ignoring proper nutrition is like trying to build a muscle-skyscraper with toothpicks and wishes – good luck with that!
Muscle growth, or hypertrophy, is a complex process demanding a strategic approach to nutrition, encompassing a balanced intake of macronutrients, sufficient calories, and meticulous attention to hydration and recovery.
Macronutrient Requirements for Muscle Growth
Meeting your macronutrient needs is crucial for muscle growth. Protein is the king, carbohydrates are the queen, and fats are the supportive royal family. Let’s break it down. Protein provides the amino acids that are the building blocks of muscle tissue. Carbohydrates offer the readily available energy your muscles need during workouts and for recovery.
Fats, often misunderstood, are essential for hormone production and overall health, supporting the entire muscle-building process. While the exact ratios vary depending on individual factors like activity level and body composition, a general guideline suggests aiming for a daily intake of 1.6-2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, a moderate amount of carbohydrates to fuel your workouts, and healthy fats to support overall well-being.
For example, a 70kg individual might aim for 112-154 grams of protein daily.
Calorie Intake for Muscle Hypertrophy
Simply put, you need to consume more calories than you burn to build muscle. This is called a caloric surplus. If you’re constantly in a calorie deficit, your body will prioritize energy conservation, making muscle growth extremely difficult. The exact caloric surplus needed will vary depending on individual metabolism and training intensity. A good starting point is to add 250-500 calories to your maintenance level, monitoring progress and adjusting accordingly.
Think of it like this: you’re giving your body the extra fuel it needs to build that impressive muscle mass.
Examples of Muscle-Building Meals and Snacks
Here are some meal and snack ideas to support your muscle growth and recovery:
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with protein powder, berries, and nuts.
- Lunch: Chicken breast salad with quinoa and avocado.
- Dinner: Lean beef stir-fry with brown rice and vegetables.
- Snacks: Greek yogurt with fruit, protein shake, hard-boiled eggs, almonds.
These examples provide a good balance of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to fuel your workouts and support muscle recovery.
The Role of Sleep and Stress Management in Muscle Recovery
Sleep isn’t just for the lazy; it’s crucial for muscle recovery and growth. During sleep, your body releases growth hormone, which plays a vital role in muscle protein synthesis. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Stress, on the other hand, can hinder muscle growth by increasing cortisol levels, a hormone that can break down muscle tissue.
Practicing stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature can significantly improve recovery. Imagine your muscles as a team of hardworking construction workers; they need rest and relaxation to rebuild and get stronger.
Optimizing Hydration for Muscle Growth
Water is essential for numerous bodily functions, including nutrient transport, waste removal, and temperature regulation. Dehydration can impair muscle function and hinder recovery. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially before, during, and after workouts. You can also incorporate hydrating electrolytes if you engage in intense or prolonged training sessions. Think of water as the lubricant that keeps your muscle-building machine running smoothly.
Want to pack on muscle faster than a cheetah on caffeine? Effective weight lifting routines are key, focusing on compound movements and progressive overload. But finding the best plan can feel like searching for the Holy Grail of gains! That’s where a solid strength training program comes in, like the one you can find at best strength training program , to guide your muscle-building journey.
Then, get back to those iron-pumping sessions!
Advanced Training Techniques
So, you’ve mastered the basics, sculpted your biceps into magnificent peaks, and your quads could rival a prize-winning Clydesdale. Congratulations! But to truly unlock your inner muscle-bound übermensch, you need to delve into the arcane arts of advanced training techniques. Think of it as graduating from weightlifting 101 to weightlifting ninja warrior.Periodization: The Art of Planned Muscle MayhemPeriodization is essentially the strategic manipulation of your training variables (volume, intensity, frequency, rest) over time to optimize muscle growth and prevent plateaus.
Imagine it as a carefully orchestrated symphony of sweat and gains, not a chaotic mosh pit of random exercises. Instead of hammering your muscles with the same routine endlessly, periodization involves cycling through different phases, each with specific goals. For example, you might start with a hypertrophy phase focused on building muscle size, followed by a strength phase to increase your lifting capacity, and finally a peaking phase to maximize performance before a competition (or a particularly important beach trip).
This prevents overtraining and keeps your muscles guessing, ensuring continued progress.
Periodization Principles in Weightlifting
Periodization involves several key principles. Macrocycles are the big picture – the overall yearly plan. Mesocycles are the medium-term phases within a macrocycle (e.g., hypertrophy, strength). Microcycles are the short-term weekly or monthly plans within a mesocycle. Each phase targets specific adaptations using different training variables.
For instance, a hypertrophy phase might involve higher reps and sets with moderate weight, while a strength phase would emphasize lower reps with heavier weight. Careful planning and progression are crucial for success. Ignoring periodization is like trying to build a house without a blueprint – you might get something vaguely resembling a structure, but it’ll probably collapse under its own weight (or lack thereof).
Training Splits: Full Body vs. Upper/Lower and Beyond
The choice of training split depends on your goals, experience level, and recovery capacity. A full-body workout hits all muscle groups in each session, ideal for beginners or those with limited time. However, it can lead to fatigue if not properly managed. Upper/lower splits divide workouts into upper and lower body days, allowing for more focused training volume and better recovery.
Other splits, such as push/pull/legs, further segment muscle groups, optimizing intensity and allowing for more specialized training. The “best” split is the one you can consistently adhere to and that promotes continuous progress. Sticking to a suboptimal routine consistently is better than inconsistently following an optimal one.
Advanced Training Techniques: Unlocking Muscle Growth’s Secret Codes
Advanced training techniques can supercharge your gains by pushing your muscles beyond their comfort zones. Drop sets involve reducing the weight after reaching muscle failure, continuing until failure again. Supersets pair two exercises targeting opposing muscle groups (e.g., biceps curls and triceps extensions) back-to-back with minimal rest. Rest-pause sets involve taking short breaks during a set to allow for further repetitions beyond initial failure.
These techniques increase time under tension, metabolic stress, and muscle damage, all contributing to muscle growth. However, they should be used strategically and not every session, as they increase the risk of overtraining.
Exercise Progression and Tracking: Charting Your Gains
Tracking your progress is crucial for making informed decisions about your training. This isn’t just about vanity metrics; it’s about understanding what works and what doesn’t. Keep a training log, noting the exercises, sets, reps, weight, and your perceived exertion. Gradually increase the weight, reps, or sets over time (progressive overload) to challenge your muscles and stimulate further growth.
This could involve adding weight to the bar, increasing the number of repetitions, adding another set, or reducing rest periods. Failing to track your progress is like sailing without a compass – you might eventually reach land, but it’ll be a much longer, more arduous journey.
Sample Periodization Plan (Visual Representation)
Imagine a chart with three columns representing Macrocycle (Year), Mesocycle (12 weeks), and Microcycle (Weekly). The Macrocycle shows the overall yearly goal (e.g., significant muscle gain). Each Mesocycle represents a phase (e.g., Hypertrophy, Strength, Power). Within each Mesocycle, the Microcycles detail the weekly workouts, specifying the training split (e.g., Upper/Lower), exercises, sets, reps, and rest periods. The chart visually demonstrates the progression of training intensity and volume across the year, starting with a higher volume, lower intensity phase for hypertrophy, gradually shifting to a lower volume, higher intensity phase for strength, and then potentially a peaking phase with a reduced volume and high intensity.
The visual representation clearly shows the cyclical nature of periodization, emphasizing the planned variation in training variables over time to optimize results.
Final Summary: Effective Weight Lifting Routines For Building Muscle Mass Quickly
So, there you have it – your roadmap to a faster, more efficient path to muscle growth. Remember, building muscle isn’t just about lifting heavy; it’s a holistic process that involves strategic training, mindful nutrition, and consistent effort. Embrace the challenge, celebrate the small victories, and watch as your dedication transforms not only your physique but also your confidence.
Now go forth and conquer those weights! (But remember to stretch… seriously.)