Effective weight training workout plans for rapid weight loss: Forget the fad diets and embrace the iron! This isn’t your grandma’s aerobics class; we’re talking about sculpting a leaner, meaner you through the power of weights. Prepare to ditch the wobbly bits and unleash your inner superhero – because building muscle isn’t just about looking good, it’s about feeling amazing.
We’ll delve into the science, the strategy, and the sheer satisfaction of transforming your body through a carefully crafted weight training program designed for rapid results. Get ready to sweat, lift, and conquer those goals!
This guide will equip you with a 12-week weight training program, complete with a detailed exercise plan, nutritional advice that won’t leave you hangry, and a smart approach to cardio that complements your strength training. We’ll also tackle crucial aspects like injury prevention, proper form, and how to avoid those pesky weight-loss plateaus. Think of it as your personal trainer, nutritionist, and motivational coach all rolled into one—but without the hefty price tag.
Introduction to Weight Training for Weight Loss

So, you want to shed those extra pounds and sculpt a physique that would make Michelangelo weep with joy? Forget the fad diets and questionable juice cleanses – let’s talk about the power of weight training for weight loss. It’s not just about building bulging biceps; it’s a scientifically proven method to melt fat and build lean muscle mass, leaving you feeling stronger and more confident than ever.Weight training, unlike steady-state cardio alone, boosts your metabolism in a way that keeps burning calories even after your workout is done.
This is due to the increased muscle mass you build. Muscle tissue is metabolically active, meaning it requires more energy to maintain itself compared to fat tissue. The more muscle you have, the more calories your body burns at rest, leading to a higher overall calorie deficit and thus, weight loss. This phenomenon is often referred to as the “afterburn effect” or Excess Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption (EPOC).
Furthermore, weight training improves insulin sensitivity, helping your body regulate blood sugar levels more effectively and preventing fat storage.
The History of Weight Training and Weight Management
While the ancient Greeks and Romans certainly engaged in forms of strength training, the modern understanding and application of weight training for weight loss is a relatively recent development. Early weight training focused primarily on strength and bodybuilding, with weight loss often considered a secondary benefit. However, as our understanding of physiology improved, so did the recognition of weight training’s crucial role in metabolic health and weight management.
The shift towards incorporating weight training into comprehensive weight loss programs became increasingly prominent in the latter half of the 20th century, particularly with the rise of fitness science and research emphasizing the importance of muscle mass in overall health and weight regulation. The modern fitness landscape now widely embraces weight training as an essential component of any effective weight loss strategy.
Types of Weight Training for Weight Loss
Choosing the right weight training style depends on your fitness level, goals, and preferences. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach, but several popular methods can effectively contribute to weight loss.A good starting point for beginners is a full-body workout routine that targets all major muscle groups (legs, chest, back, shoulders, arms) two or three times a week. This approach promotes overall strength development and calorie expenditure.
Imagine a workout where you perform squats, bench presses, rows, overhead presses, and bicep curls, focusing on proper form and controlled movements.For those seeking a more advanced approach, split routines can be beneficial. These routines divide the workout across different muscle groups on separate days, allowing for more focused training and greater volume. For instance, one day could focus on chest and triceps, another on back and biceps, and another on legs and shoulders.
This approach requires more time commitment but can lead to significant muscle growth and fat loss.Circuit training is another fantastic option. This involves moving quickly between different exercises with minimal rest, creating a high-intensity metabolic workout that burns a significant amount of calories and improves cardiovascular fitness. Picture yourself rapidly transitioning between squats, push-ups, burpees, and rows, keeping your heart rate elevated throughout the session.Finally, remember that consistency is key.
Ditch the fad diets! Effective weight training workout plans for rapid weight loss hinge on building muscle, which boosts your metabolism. To find the perfect plan for you, check out the best strength training program to discover the secrets of sculpting a leaner, meaner you. Remember, consistency is key – so find a program you’ll actually stick with for effective, long-term weight loss.
Regardless of the style you choose, sticking to a regular weight training schedule is crucial for achieving your weight loss goals.
Designing a Weight Training Program for Rapid Weight Loss
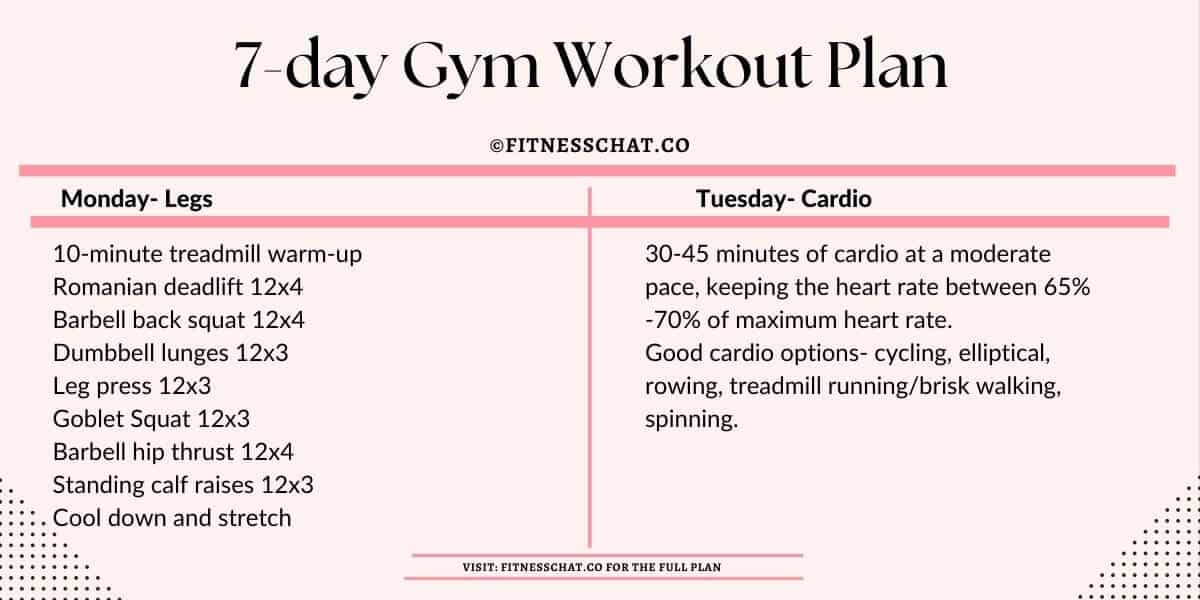
So, you’re ready to sculpt your physique while shedding those extra pounds? Fantastic! Weight training isn’t just about building muscle; it’s a powerful tool for boosting your metabolism and torching calories, even after your workout is done. This program focuses on building a solid foundation for beginners, leading to noticeable changes in your body composition and energy levels.
Remember, consistency is key – think of this as a marathon, not a sprint (unless you’re sprinting to the gym, which is also encouraged!).
A Sample 12-Week Weight Training Program for Beginners
This program prioritizes compound movements – exercises that work multiple muscle groups simultaneously – to maximize calorie burn and overall strength gains. We’ll focus on building a strong base before gradually increasing intensity. Remember to consult your doctor before starting any new workout routine. Listen to your body, and don’t hesitate to adjust the program based on your individual needs and progress.
| Week | Exercise | Sets | Reps | Rest (seconds) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-4 (Beginner Phase) | Squats | 3 | 10-12 | 60 |
| 1-4 | Push-ups (modified on knees if needed) | 3 | As many as possible (AMRAP) | 45 |
| 1-4 | Rows (using resistance bands or dumbbells) | 3 | 10-12 | 60 |
| 1-4 | Plank | 3 | 30-60 seconds hold | 30 |
| 5-8 (Intermediate Phase) | Squats | 3 | 12-15 | 60 |
| 5-8 | Push-ups | 3 | AMRAP | 45 |
| 5-8 | Bent-over Rows (dumbbells or barbell) | 3 | 12-15 | 60 |
| 5-8 | Walking Lunges | 3 | 10-12 per leg | 60 |
| 9-12 (Advanced Phase) | Barbell Squats | 4 | 8-12 | 90 |
| 9-12 | Bench Press | 4 | 8-12 | 90 |
| 9-12 | Deadlifts | 1 | 5 | 120 |
| 9-12 | Overhead Press | 4 | 8-12 | 90 |
The Importance of Progressive Overload in a Weight Loss Program
Progressive overload is the gradual increase in the demands placed on your muscles over time. This could mean lifting heavier weights, increasing the number of repetitions, adding sets, or decreasing rest periods. Think of it as constantly challenging your body to adapt and grow stronger. Without progressive overload, your body plateaus, and your weight loss progress stalls. For example, if you’re consistently lifting the same weight for the same number of reps, your muscles become accustomed to the load, hindering further progress.
Want to melt fat like an ice cube in the Sahara? Effective weight training workout plans for rapid weight loss often involve high-intensity interval training, but building serious muscle is key. To truly maximize your results, check out this amazing resource on effective weight training program for increasing muscle strength and power – stronger muscles burn more calories, even at rest! So, ditch the flab and embrace the gains for a leaner, meaner you.
By gradually increasing the weight or reps each week (or every few weeks), you continue to stimulate muscle growth and calorie burning.
The Role of Compound Exercises Versus Isolation Exercises in Maximizing Calorie Expenditure
Compound exercises, like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses, work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, resulting in a significantly higher calorie burn during and after your workout. Isolation exercises, such as bicep curls or tricep extensions, focus on a single muscle group. While they have their place in a well-rounded program, compound exercises are far more effective for maximizing calorie expenditure and promoting overall weight loss.
For instance, a single set of squats engages your quads, hamstrings, glutes, and core, significantly increasing your metabolic rate compared to a set of bicep curls. The increased muscle mass from compound exercises also contributes to a higher resting metabolic rate, meaning you burn more calories even when you’re at rest.
Nutritional Considerations for Weight Loss with Weight Training
Let’s be honest, weight training is the muscle-building, calorie-torching superhero of fitness, but it needs a trusty sidekick: nutrition. Think of your weight training program as a finely tuned engine; without the right fuel (food!), it’s going to sputter and stall. Proper nutrition isn’t just about shedding pounds; it’s about building lean muscle, boosting energy, and feeling fantastic throughout your 12-week journey.
Get ready to discover the delicious secrets to fueling your fitness success!
Macronutrient Balance for Weight Loss and Muscle Preservation
Maintaining a balanced intake of macronutrients—protein, carbohydrates, and fats—is crucial for both weight loss and muscle growth. Think of it like this: protein is the building block for your muscles, carbohydrates provide the energy for your workouts, and healthy fats support hormone production and overall health. A severely restrictive diet will leave you feeling weak, depleted, and possibly even sabotaging your muscle-building efforts.
The ideal ratio will vary depending on individual needs and goals, but a common recommendation for weight loss with muscle preservation is a higher protein intake (around 1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight), moderate carbohydrate intake (adjusting based on activity levels), and a healthy amount of unsaturated fats. Remember, consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist can help personalize your macronutrient plan for optimal results.
Don’t be afraid to experiment to find what works best for your body and lifestyle.
Sample Meal Plan for a 12-Week Weight Training Program
This sample meal plan is a guideline and may need adjustment based on individual caloric needs and preferences. Remember, consistency is key!
This plan emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, providing a good balance of protein, carbohydrates, and healthy fats to support your weight training program and overall health. Remember to adjust portion sizes based on your individual caloric needs and activity levels.
- Breakfast (approx. 400 calories): Oatmeal with berries and nuts, Greek yogurt with fruit and a sprinkle of granola, or a protein smoothie with spinach, banana, and protein powder.
- Lunch (approx. 500 calories): Large salad with grilled chicken or fish, quinoa or brown rice bowl with vegetables and lean protein, or a whole-wheat wrap with hummus, vegetables, and lean protein.
- Dinner (approx. 600 calories): Baked salmon with roasted vegetables, lean ground turkey stir-fry with brown rice, or chicken breast with sweet potato and broccoli.
- Snacks (approx. 200 calories total): A handful of almonds, a piece of fruit, Greek yogurt, or a protein bar (choose one with low sugar and high protein).
Potential Nutritional Pitfalls to Avoid During Weight Loss
Avoiding common nutritional pitfalls is essential for maximizing your weight loss results and preventing plateaus.
Many people fall into traps that hinder their progress. Understanding these common mistakes is the first step towards avoiding them.
- Crash Dieting: Severely restricting calories can lead to muscle loss, fatigue, and metabolic slowdown. Instead, focus on a sustainable calorie deficit through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Skipping Meals: This can lead to overeating later in the day and hinder your metabolism. Regular meals help maintain energy levels and blood sugar stability.
- Neglecting Hydration: Water is crucial for overall health, aiding digestion, and preventing muscle cramps. Aim for at least eight glasses of water per day.
- Excessive Processed Foods: These are often high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and sodium, contributing to weight gain and inflammation. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods.
- Insufficient Protein Intake: Inadequate protein intake can hinder muscle growth and repair, impacting your weight training progress. Ensure you’re consuming enough protein to support your workouts.
Cardiovascular Exercise Integration
So, you’ve sculpted your muscles like a Greek god (or goddess!), but the journey to rapid weight loss isn’t solely a weight room rendezvous. Cardio, my friend, is the cherry on top of that sculpted sundae. It’s the secret ingredient that boosts your metabolism, burns extra calories, and helps you achieve that lean, mean, weight-loss machine physique. Let’s dive into how to seamlessly integrate cardio into your already awesome weight training routine.Combining weight training with cardio is like peanut butter and jelly – a match made in fitness heaven.
But just like there are many types of peanut butter (crunchy, smooth, etc.), there are different types of cardio, each offering unique benefits. Choosing the right type and integrating it effectively is key to maximizing your weight loss results. Think of it as strategic calorie torching, where we’re not just burning calories during the workout, but also revving up your metabolism for hours afterward, leading to greater fat loss.
Comparison of HIIT and Steady-State Cardio Benefits
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods. Think sprinting for 30 seconds, then walking for 60 seconds, repeated several times. Steady-state cardio, on the other hand, is a consistent pace of moderate-intensity exercise, like jogging at a steady pace for 30 minutes. HIIT is fantastic for burning a significant number of calories in a shorter amount of time, and it also boosts your metabolism significantly post-workout.
Steady-state cardio, while less intense, is excellent for improving cardiovascular health and endurance, and can be easier to maintain over a longer period. The best approach often involves a combination of both, leveraging the strengths of each. For example, incorporating HIIT twice a week for intense calorie burn, and steady-state cardio on other days for improved endurance and recovery.
Structuring a Weekly Workout Schedule
A well-structured workout schedule is crucial for maximizing results and preventing burnout. It’s all about finding the sweet spot between challenging your body and allowing it adequate time to recover. Remember, rest is just as important as the workout itself! A balanced approach ensures you don’t overtrain, leading to plateaus or even injuries. We’ll aim for a schedule that allows for muscle growth and recovery from weight training while also incorporating sufficient cardio for calorie expenditure and cardiovascular health improvements.
The key is consistency and listening to your body.
Ditch the fad diets and embrace the iron! Effective weight training workout plans for rapid weight loss aren’t just about cardio; they’re about building muscle, which boosts your metabolism like a caffeinated kangaroo. For women specifically, finding a routine that targets all the right areas is key, and that’s where a fantastic resource like this effective strength training workout routine for women comes in handy.
Ultimately, sculpting a stronger you leads to a leaner, meaner, and more powerful you – all part of a truly effective weight training workout plan.
Sample Weekly Workout Schedule
Here’s a sample schedule, but remember to adjust it based on your fitness level and personal preferences. It’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional or certified trainer before starting any new workout routine.
- Monday: Weight Training (Upper Body)
- Tuesday: Steady-State Cardio (30 minutes brisk walking or jogging)
- Wednesday: Rest or Active Recovery (light stretching, yoga)
- Thursday: Weight Training (Lower Body)
- Friday: HIIT (20-30 minutes, alternating high-intensity bursts with short recovery periods)
- Saturday: Long, slow cardio (45-60 minutes at a moderate pace – cycling, swimming, etc.)
- Sunday: Rest
Remember, this is just a template. You can adjust the intensity, duration, and types of cardio based on your goals and how your body responds. The key is consistency and finding a routine that you can stick with long-term. Don’t be afraid to experiment and find what works best for you! Listen to your body, and remember that progress, not perfection, is the goal.
Rest and Recovery for Optimal Results
Think of your body like a finely tuned sports car – pushing it relentlessly without proper maintenance will lead to a breakdown, not a victory lap. Rest and recovery aren’t optional extras in your weight loss journey; they’re the high-octane fuel that powers your progress. Ignoring this crucial element will not only hinder your weight loss but also increase your risk of injury and burnout.Adequate rest is vital for muscle growth and repair.
Dreaming of sculpted biceps and a smaller waistline? Effective weight training workout plans for rapid weight loss aren’t just about grunting and groaning; they’re about smart planning. If you’re a newbie, though, check out this fantastic guide for beginners: strength training for weight loss: a complete beginner’s guide , before diving headfirst into intense routines. Then, armed with knowledge, you can craft those effective weight training plans for rapid weight loss and conquer your fitness goals!
When you lift weights, you’re actually causing microscopic tears in your muscle fibers. It’s during rest periods that your body repairs these tears, making your muscles stronger and more resilient. This process also plays a significant role in fat loss, as muscle tissue burns more calories at rest than fat tissue. Sleep deprivation disrupts this crucial repair and rebuilding process, hindering your progress and potentially increasing your cravings for high-calorie, comfort foods.
The Importance of Sleep and Adequate Rest in Muscle Recovery and Weight Loss
Sufficient sleep (7-9 hours per night) is paramount. During sleep, your body releases hormones that promote muscle growth and repair, such as human growth hormone (HGH). Lack of sleep leads to lower HGH levels, impaired muscle protein synthesis, and increased cortisol (a stress hormone that can hinder fat loss and muscle growth). Aim for consistent sleep patterns to optimize your body’s natural recovery processes.
Think of sleep as your body’s nightly weight loss and muscle building factory – keep it running smoothly for optimal results. For example, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that individuals who slept less than 5 hours per night had a significantly higher risk of obesity compared to those who slept 7-9 hours.
Signs and Symptoms of Overtraining and How to Avoid It
Overtraining is like hitting the gas pedal without ever letting up. Your body will eventually give up, leading to plateaus, injuries, and even illness. Common signs include persistent fatigue, decreased performance, increased resting heart rate, muscle soreness that doesn’t improve with rest, irritability, and difficulty sleeping. To avoid overtraining, prioritize progressive overload (gradually increasing the intensity or volume of your workouts), incorporate rest days into your training schedule, listen to your body, and don’t be afraid to take a break when needed.
A structured training plan with built-in deloading periods (weeks of reduced training volume) can help prevent overtraining and maintain long-term progress. For instance, a professional athlete might follow a 12-week training cycle with a deload week every 4 weeks to avoid burnout.
Strategies for Managing Stress Levels to Enhance Recovery and Prevent Plateaus
Stress is a silent saboteur of your weight loss goals. Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can increase appetite, promote fat storage, and impair muscle recovery. Managing stress is crucial for optimizing your body’s ability to repair and rebuild. Effective strategies include incorporating stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, spending time in nature, listening to calming music, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy.
Prioritizing self-care, such as getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and maintaining social connections, also plays a crucial role in stress management. For example, practicing mindfulness meditation for just 10-15 minutes daily can significantly reduce stress hormones and improve overall well-being, thus supporting your weight loss efforts. Finding healthy coping mechanisms will not only improve your recovery but also contribute to a more positive and sustainable weight loss journey.
Safety and Injury Prevention
Weight training, while incredibly effective for weight loss, isn’t a walk in the park. It involves manipulating heavy objects, and if not approached with respect and proper technique, can lead to injuries ranging from minor aches to serious setbacks. Think of it like driving a sports car – exhilarating, but requires skill and caution to avoid a crash.
This section will equip you with the knowledge to keep your weightlifting journey safe and injury-free, allowing you to reap the rewards without the pain.Proper form and technique are paramount to avoid injury and maximize results. Ignoring this crucial aspect is like trying to bake a cake without following the recipe – you might end up with a culinary disaster.
Understanding and consistently applying correct form will protect your joints, muscles, and overall well-being. Furthermore, selecting appropriate weights is equally important; it’s not a competition to see how much you can lift, but rather a strategic process to achieve your goals safely and effectively.
Common Weight Training Injuries and Prevention Strategies
Common weight training injuries include muscle strains (pulled muscles), sprains (ligament injuries), tendonitis (inflammation of tendons), and back pain. These often stem from improper form, using excessive weight, neglecting warm-up and cool-down routines, and insufficient rest. Prevention involves a multi-pronged approach: thorough warm-ups preparing your body for the workout, gradual progression of weight and intensity to avoid sudden stress on muscles and joints, maintaining proper form throughout each exercise, listening to your body and taking rest days when needed, and incorporating stretching into your routine to maintain flexibility and reduce muscle tightness.
Think of it as preventative maintenance for your body’s amazing machine.
Proper Form and Technique for Key Compound Exercises
Mastering proper form is crucial for safety and effectiveness. Let’s look at some key compound exercises:
Squats
Imagine a perfectly aligned body: feet shoulder-width apart, toes slightly outward, back straight, chest up, and core engaged. The movement should originate from your hips, bending your knees while keeping your weight in your heels. Avoid letting your knees cave inwards, which can put stress on your ligaments. Think of sitting back into a chair. The controlled descent and ascent are key to a safe and effective squat.
Dreaming of sculpted abs and a physique that’ll make Hercules jealous? Effective weight training workout plans for rapid weight loss aren’t just about grueling gym sessions; they’re about smart, progressive training. For newbies, starting with a solid foundation is key – check out this simple weight lifting program for beginners to lose weight to build strength and confidence before tackling more advanced routines.
Then, watch those pounds melt away as you level up your weight training game!
Deadlifts
The deadlift involves hinging at the hips, keeping your back straight, and lifting the weight using your legs and glutes. Avoid rounding your back, which can lead to serious back injuries. Imagine a straight line from your head to your heels throughout the movement. Start with a light weight to perfect your form before increasing the load.
This is not a “lift as much as you can” exercise but a controlled movement.
Want to melt fat like an ice cube in a sauna? Effective weight training workout plans for rapid weight loss hinge on building serious muscle. That’s where incorporating killer exercises like those found at muscular strength exercises comes in; they’ll boost your metabolism and sculpt you into a lean, mean, weight-loss machine. Remember, it’s not just about shedding pounds; it’s about building a body that burns calories even when you’re napping!
Bench Press
Lie flat on the bench with your feet flat on the floor. Grip the bar slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, lower the bar to your chest with controlled movement, and push it back up. Avoid bouncing the bar off your chest and keep your elbows slightly tucked in. Maintain a stable core throughout the lift.
Overhead Press
Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding the bar at shoulder height. Press the bar overhead, keeping your core engaged and avoiding arching your back. The movement should be controlled and smooth, not jerky or forceful. Lower the bar back down slowly and with control. Maintaining a stable core is vital throughout the lift.
Selecting Appropriate Weights and Avoiding Excessive Exertion
Start with weights that allow you to maintain proper form for the recommended number of repetitions. It’s better to lift lighter weights with perfect form than heavier weights with poor form. Gradually increase the weight as you get stronger. Listen to your body. Pain is a warning sign; don’t push through it.
Rest and recovery are just as important as the workout itself. Think of your body like a finely tuned engine; it needs fuel (nutrition), maintenance (rest), and appropriate workload (weight training) to perform optimally. Ignoring any of these elements can lead to burnout and injury.
Tracking Progress and Making Adjustments: Effective Weight Training Workout Plans For Rapid Weight Loss
So, you’ve started your weight training journey, and you’re feeling fantastic (or at least, less like a melted marshmallow). But feeling good isn’t enough; you need a system to monitor your progress and tweak your plan as you become a lean, mean, weight-lifting machine. Without tracking, you’re essentially navigating a weight loss maze blindfolded, hoping for the best. Don’t be that person.Tracking your progress isn’t just about the numbers on the scale; it’s about celebrating your victories and identifying areas for improvement.
Think of it as a progress report from your awesome self to your awesome self.
Methods for Tracking Weight, Body Measurements, and Workout Performance, Effective weight training workout plans for rapid weight loss
To effectively track your progress, a multi-pronged approach is crucial. Relying solely on the scale can be misleading, as muscle weighs more than fat. A comprehensive system provides a clearer picture of your transformation.
- Weight: Weigh yourself weekly, at the same time of day, preferably in the morning before breakfast. Record this in a journal or app. Remember, fluctuations are normal; focus on the overall trend.
- Body Measurements: Measure your waist, hips, thighs, and arms (or any areas you want to target). Use a measuring tape and record these measurements weekly alongside your weight. Changes in these measurements often precede changes on the scale, offering early indicators of success.
- Workout Performance: Track the weight you lift, the number of repetitions and sets you complete, and the amount of rest you take between sets. This helps you monitor your strength gains and identify areas where you can progressively overload (gradually increasing the weight, reps, or sets). A simple spreadsheet or training logbook works wonders.
Adjusting the Weight Training Program Based on Progress and Individual Needs
Your weight training program isn’t set in stone; it’s a dynamic tool that should adapt to your evolving needs. If you’re not seeing progress, don’t just keep doing the same thing expecting different results (that’s the definition of insanity, right?).For example, if you’ve been consistently hitting your reps and sets with ease for several weeks, it’s time to increase the weight, add more reps, or increase the number of sets.
Conversely, if you’re struggling to complete your sets with good form, you might need to decrease the weight or focus on improving your technique before increasing the challenge. Listen to your body!
Identifying and Overcoming Weight Loss Plateaus
Plateaus are inevitable. They’re the weight loss equivalent of hitting a brick wall. Don’t panic! It simply means your body has adapted to your current routine, and it’s time to shake things up.Strategies to overcome plateaus include:
- Change your workout routine: Try different exercises, vary the order of exercises, or incorporate new training techniques like drop sets or supersets. This shocks your muscles and keeps your body guessing.
- Adjust your caloric intake: A slight reduction in calories can help jumpstart your weight loss again. Consult a nutritionist or dietitian for personalized guidance.
- Prioritize sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can negatively impact weight loss. Incorporate stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
Remember, consistency is key. Even small adjustments can make a big difference over time. Keep tracking, keep adapting, and keep crushing those goals!
Visual Aids
Let’s face it, reading about proper exercise form is about as exciting as watching paint dry. But fear not, aspiring weight-loss warriors! We’re going to paint a vivid picture (with words, of course) of perfect form for three crucial exercises, so you can visualize your way to a fitter, stronger you. Think of this as a mental workout before the physical one.
Barbell Squat
Imagine yourself standing with feet slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, toes pointing slightly outward. Your back should be straight, like a proud, unbent ruler, engaging your core muscles to maintain this posture throughout the movement. Now, imagine slowly lowering yourself down as if sitting in an invisible chair, keeping your weight in your heels. Your knees should track over your toes, avoiding any inward or outward collapsing.
The depth of your squat should be such that your thighs are parallel to the ground, or even slightly below, if your flexibility allows. As you descend, keep your chest up and maintain that straight back. The ascent is the reverse of the descent – a powerful push through your heels, returning to the starting position with control.
Think of it as a graceful, powerful dance with the barbell.
Dumbbell Bench Press
Lie on a bench, feet flat on the floor, and grip a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing your feet. Your grip should be slightly wider than shoulder-width apart. Imagine your back firmly pressed against the bench, creating a straight line from your head to your hips – avoid arching your back excessively. Before you begin, take a deep breath, filling your lungs like a balloon.
Slowly lower the dumbbells towards your chest, keeping your elbows slightly bent to avoid locking your joints. As you lower the weight, exhale slowly and deliberately. Push the dumbbells back up to the starting position, again maintaining a steady and controlled movement. The key here is to engage your chest muscles and maintain a stable posture. This isn’t a frantic flailing of weights; it’s a controlled and powerful movement.
Dumbbell Row
Start by bending at the hips, maintaining a straight back (that ruler image again!). Let your torso hang almost parallel to the ground, keeping your core engaged. Grab a dumbbell in each hand, palms facing your body. Imagine pulling the dumbbells up towards your chest, keeping your elbows close to your body. Squeeze your shoulder blades together at the top of the movement, feeling the tension in your back muscles.
Slowly lower the dumbbells back to the starting position, maintaining control throughout. The movement should feel deliberate and focused, not jerky or rushed. Think of your body as a lever, and your back muscles as the powerful engine pulling the weight.
Final Conclusion
So, there you have it – your blueprint for rapid weight loss through effective weight training. Remember, this isn’t a race; it’s a transformation. Embrace the journey, celebrate your progress, and don’t be afraid to adjust the plan to suit your individual needs. Listen to your body, fuel it right, and watch as you shed pounds and gain strength, confidence, and a whole new appreciation for the incredible power of weight training.
Now go forth and conquer those weights!
