Weight training for weight gain and muscle building: Forget skinny jeans and embrace the gains! This isn’t your grandpappy’s weightlifting; we’re talking about sculpting a physique worthy of a Greek god (or goddess, of course!). We’ll delve into the science behind muscle growth, crafting a program that’s as effective as it is enjoyable, and fueling your body with the right nutrients to maximize results.
Prepare to unleash your inner powerhouse!
We’ll cover everything from choosing the right exercises and mastering proper form to designing a personalized workout plan and understanding the crucial role of nutrition. Think of this as your all-access pass to a stronger, more sculpted you – no expensive gym memberships or confusing supplements required (although, we’ll touch on those too!). Get ready to lift heavier, eat smarter, and transform your body.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Weight Training for Muscle Growth
So, you want to build some serious muscle, huh? Forget the magic pills and the snake oil salesmen – the key to packing on pounds of lean muscle lies in understanding how your body actually works. This isn’t rocket science (although it
is* surprisingly complex biochemistry), but with a little knowledge, you can sculpt yourself into the magnificent specimen you’ve always dreamed of.
Muscle Hypertrophy: The Science of Getting Bigger
Muscle growth, or hypertrophy, is essentially a process of controlled damage and repair. When you lift weights, you’re creating tiny tears in your muscle fibers. This isn’t bad; it’s the signal your body needs to start the rebuilding process. Your body responds by synthesizing new muscle proteins, making the fibers thicker and stronger. This increased protein synthesis, coupled with a reduction in protein breakdown, leads to the increase in muscle size we all crave.
Think of it like a beautifully orchestrated demolition and reconstruction project, all happening within your muscles. The key is to provide the right stimulus (weight training) and adequate recovery (rest and nutrition).
Progressive Overload: The Engine of Muscle Growth
Imagine trying to build a skyscraper with only a shovel. You’d get nowhere fast. Similarly, your muscles need a constantly increasing challenge to continue growing. Progressive overload is the principle of gradually increasing the demands placed on your muscles over time. This can be done by increasing the weight lifted, the number of repetitions, or the number of sets.
It’s about consistently pushing your limits, forcing your muscles to adapt and grow stronger to meet the new challenge. Without progressive overload, your muscles will plateau, and your gains will stagnate – a fate worse than death for any serious lifter.
Muscle Fiber Types and Their Response to Training
Your muscles aren’t a homogenous blob; they’re made up of different types of muscle fibers, each with its own characteristics. Type I fibers, also known as slow-twitch fibers, are endurance-oriented and resist fatigue. Type II fibers, or fast-twitch fibers, are powerful but tire more quickly. These are further subdivided into Type IIa (intermediate) and Type IIx (fastest).
Weight training stimulates both types, but the emphasis depends on the training style. Higher-rep training tends to engage Type I fibers more, while lower-rep, heavier weight training predominantly targets Type II fibers. The ideal training program balances both for optimal muscle growth.
Comparison of Training Styles for Muscle Growth
Understanding different training styles helps tailor your approach for optimal results. Here’s a comparison:
| Training Style | Rep Range | Set Range | Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powerlifting | 1-5 | 3-5 | Strength and maximal force production |
| Bodybuilding | 6-12 | 3-4 | Muscle hypertrophy and aesthetics |
| Strongman | Variable, often low reps | Variable, often high volume | Overall strength, functional strength, and size |
Designing a Weight Training Program for Weight Gain and Muscle Building
So, you’re ready to sculpt yourself into a magnificent specimen of human fitness? Excellent! But throwing weights around willy-nilly won’t magically transform you into the next Arnold Schwarzenegger (though we appreciate the ambition). A well-structured program is key – think of it as the architectural blueprint for your new, muscular physique. We’ll guide you through designing a plan that’s both effective and (dare we say it) enjoyable.
A Sample 12-Week Weight Training Program for Beginners, Weight training for weight gain and muscle building
This program focuses on compound exercises – movements that work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, maximizing your bang for your buck (and your calorie burn!). Remember, consistency is king! Don’t aim for perfection, aim for progress.
| Week | Monday | Wednesday | Friday |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-4 | Squats (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Bench Press (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Bent-Over Rows (3 sets of 8-12 reps) | Overhead Press (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Deadlifts (1 set of 5 reps, 1 set of 3 reps, 1 set of 1 rep), Pull-ups (3 sets to failure, or assisted pull-ups) | Rest or light cardio |
| 5-8 | Squats (3 sets of 10-15 reps), Incline Bench Press (3 sets of 10-15 reps), Barbell Rows (3 sets of 10-15 reps) | Overhead Press (3 sets of 10-15 reps), Deadlifts (1 set of 5 reps, 1 set of 3 reps, 1 set of 1 rep), Pull-ups (3 sets to failure, or assisted pull-ups) | Rest or light cardio |
| 9-12 | Front Squats (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Decline Bench Press (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Dumbbell Rows (3 sets of 8-12 reps) | Overhead Press (3 sets of 8-12 reps), Romanian Deadlifts (3 sets of 10-15 reps), Lat Pulldowns (3 sets of 10-15 reps) | Rest or light cardio |
Incorporating Progressive Overload
Progressive overload is the cornerstone of muscle growth. It simply means consistently increasing the demand placed on your muscles over time. This can be achieved by increasing the weight, reps, sets, or decreasing rest time between sets. Imagine your muscles as tiny, ambitious weightlifters; they need to be challenged to get stronger. For example, if you can comfortably do 3 sets of 10 reps of squats with 135 lbs one week, aim for 140 lbs the next week, or 3 sets of 12 reps with 135 lbs.
So you want to pack on some serious muscle, huh? Weight training for weight gain and muscle building is the name of the game, my friend! To really maximize your gains, you need to focus on building a solid foundation of strength. That’s where incorporating muscular strength exercises comes in – think squats, deadlifts, the whole shebang.
These exercises will help you lift heavier weights and build even more muscle mass, making your weight training even more effective!
Selecting Appropriate Weight and Repetitions
The “sweet spot” for muscle growth is generally considered to be 8-12 repetitions per set. However, this isn’t a rigid rule. Heavier weights (lower reps, 1-5) can build strength, while lighter weights (higher reps, 15-20) can increase muscle endurance. Start with a weight that allows you to complete the desired number of repetitions with good form, and gradually increase the weight as you get stronger.
So you want to ditch the toothpick physique and become a human granite statue? Weight training for weight gain and muscle building is your ticket to awesome-sauce gains! Check out this killer guide for men, Building muscle mass and strength through weightlifting routines for men , for some seriously swole-worthy routines. Then, get back to those barbells and become the magnificent muscle-bound marvel you were always meant to be!
Remember, proper form is paramount – avoid sacrificing form for weight.
The Importance of Rest and Recovery in Muscle Growth
Think of your muscles as delicate flowers – they need time to bloom! Muscle growth actually happens during rest, not during the workout itself. Adequate sleep (7-9 hours per night), proper nutrition, and rest days are crucial for recovery and preventing overtraining. Ignoring rest is like trying to build a house without enough bricks – you’ll never finish!
Nutrition Strategies for Optimal Muscle Growth

Packing on muscle isn’t just about lifting heavy; it’s about fueling your body like a champion weightlifter (even if you’re more of a “champion” at napping). Think of your muscles as tiny, demanding construction workers – they need the right materials to build and repair themselves. Ignoring their nutritional needs is like expecting a bricklayer to build a skyscraper with toothpicks and glue.
To build serious muscle, you need a strategic approach to nutrition, focusing on the right balance of macronutrients: protein, carbohydrates, and fats. These aren’t just buzzwords; they’re the building blocks of muscle growth and overall health. Get the ratios wrong, and your gains will be as slow as molasses in January.
Macronutrient Requirements for Muscle Growth
Protein is the undisputed king of muscle building. It provides the amino acids your body uses to repair and build new muscle tissue. Aim for a daily protein intake of around 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight. For example, a 70kg individual should consume between 112 and 154 grams of protein daily. Carbohydrates are your body’s primary energy source, fueling your intense workouts and preventing muscle breakdown.
Choose complex carbohydrates like brown rice, sweet potatoes, and oats over refined sugars. Fats are crucial for hormone production and overall health, contributing to optimal muscle growth. Include healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and olive oil in your diet.
So you want to pack on some serious muscle, huh? Weight training for weight gain is all about smart choices, not just lifting anything heavy. To truly maximize your gains, check out this awesome resource on Best weight training exercises for building strength and toning muscles – it’ll help you sculpt those gains into something truly magnificent.
Then, remember to fuel your body right for optimal muscle growth after your killer workout!
Sample Meal Plan for Muscle Growth
A well-structured meal plan is essential for consistent progress. This is a sample plan; adjust portion sizes based on your individual needs and activity level.
Remember, this is just a sample – adjust portions based on your caloric needs and preferences. Consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide a personalized plan tailored to your specific goals.
| Meal | Food | Macronutrient Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | Oatmeal with protein powder, berries, and nuts | Carbohydrates, Protein, Fats |
| Lunch | Chicken breast salad with quinoa and avocado | Protein, Carbohydrates, Fats |
| Dinner | Salmon with brown rice and steamed broccoli | Protein, Carbohydrates, Healthy Fats |
| Snacks | Greek yogurt with fruit, protein shake, hard-boiled eggs | Protein, Carbohydrates |
The Role of Supplements in Muscle Growth
Supplements can be helpful additions to a well-rounded diet, but they shouldn’t replace whole foods. Creatine, for instance, can increase strength and power output, leading to greater muscle gains. Protein powder can be a convenient way to increase your protein intake, especially if you struggle to meet your daily requirements through whole foods. However, remember that supplements are just that – supplements.
They are not magic bullets. A balanced diet and consistent training are still paramount.
Healthy Recipes for Muscle Gain
These recipes provide a delicious and nutritious way to fuel your muscle-building journey. Remember to adjust portion sizes based on your individual caloric needs.
- Chicken and Sweet Potato Stir-Fry: Combine diced chicken breast, sweet potato cubes, broccoli florets, and your favorite stir-fry sauce. This dish is packed with protein and complex carbohydrates.
- Lentil Soup: Lentils are a fantastic source of plant-based protein and fiber. Combine lentils with vegetables like carrots, celery, and onions for a hearty and nutritious soup.
- Overnight Oats with Protein Powder: Combine rolled oats, protein powder, milk (dairy or non-dairy), chia seeds, and your favorite fruits for a quick and easy breakfast.
- Salmon with Roasted Vegetables: Salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids and protein. Pair it with roasted vegetables like asparagus, Brussels sprouts, or bell peppers for a balanced meal.
Exercise Selection and Technique: Weight Training For Weight Gain And Muscle Building

Choosing the right exercises and mastering the proper form is crucial for maximizing muscle growth and minimizing injury. Think of it like building a house – you wouldn’t start constructing the roof before laying a solid foundation, would you? Similarly, focusing on fundamental movements will build a strong base for your physique.This section will delve into the best compound exercises, perfect your technique, explore the free weights vs.
machines debate, and finally, show you how to tailor your workouts to your specific goals.
Effective Compound Exercises for Overall Muscle Growth
Compound exercises, which work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, are the cornerstone of any effective weight training program for muscle growth. They’re incredibly efficient, maximizing your time and calorie burn while stimulating significant muscle protein synthesis. Think of them as the ultimate muscle-building multi-taskers.
- Squats: Targets quads, glutes, hamstrings, and core. Imagine a powerful, graceful movement that strengthens your entire lower body. Proper form involves keeping your back straight, chest up, and squatting until your thighs are parallel to the ground.
- Deadlifts: A full-body powerhouse exercise working your back, legs, and core. Picture a smooth, controlled lift from the floor, engaging your entire posterior chain. Maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement and focus on proper hip hinge mechanics.
- Bench Press: The king of chest exercises, also engaging shoulders and triceps. Visualize a controlled press, lowering the bar to your chest and pushing it back up with controlled power. Ensure your feet are firmly planted and your back is flat against the bench.
- Overhead Press: Works shoulders, triceps, and upper back. Imagine smoothly lifting the weight overhead, maintaining a stable core and controlled movement. Keep your elbows slightly bent to protect your shoulder joints.
- Bent-Over Rows: Targets the back muscles, including lats, rhomboids, and traps. Picture pulling the weight towards your abdomen, maintaining a straight back and controlled movement. Avoid using momentum; focus on controlled power.
Proper Form and Technique for Compound Exercises
Proper form is paramount. It’s not about how much weight you lift, but how well you lift it. Poor form can lead to injuries, hindering your progress and potentially putting you out of commission. Focus on quality over quantity – start with lighter weights to master the technique before increasing the load.
- Controlled Movements: Avoid jerky movements; each repetition should be smooth and controlled, both in the concentric (lifting) and eccentric (lowering) phases.
- Full Range of Motion: Utilize the full range of motion for each exercise to maximize muscle activation and growth. Don’t cheat the reps by using momentum.
- Proper Breathing: Inhale during the eccentric phase and exhale during the concentric phase. This helps maintain stability and control.
- Engage Your Core: Keep your core engaged throughout each exercise to maintain stability and protect your spine. Imagine bracing your abdominal muscles.
- Listen to Your Body: If you feel pain, stop immediately. Don’t push through pain; rest and recover.
Free Weights Versus Machine Exercises
The age-old debate! Both have their merits. Free weights (dumbbells, barbells) require more stabilization, engaging more muscle groups and improving balance and coordination. Machines, on the other hand, offer more stability and are generally easier to learn, making them suitable for beginners. Ideally, a balanced approach incorporating both is best.
Adjusting Exercise Selection Based on Individual Needs and Goals
Your exercise selection should be tailored to your individual needs and goals. Are you focusing on strength, hypertrophy (muscle growth), or a combination of both? Consider your experience level, any physical limitations, and your personal preferences. For example, a beginner might focus on mastering the basic compound exercises before progressing to more advanced variations. Someone with a previous injury might need to modify certain exercises or avoid them altogether.
A competitive bodybuilder might incorporate more isolation exercises to target specific muscle groups.
Tracking Progress and Making Adjustments
So, you’ve been diligently lifting weights, fueling your body like a champion, and following your meticulously crafted workout plan. But are you actuallygetting* anywhere? Tracking your progress isn’t just about seeing numbers go up; it’s about understanding your body’s response to training and making smart adjustments to keep those gains coming. Think of it as your personal muscle-building GPS – guiding you towards your ultimate physique destination.Tracking your workouts isn’t about obsessive micromanagement; it’s about informed decision-making.
Regularly monitoring your progress allows you to identify what’s working and what’s not, preventing you from wasting time on ineffective exercises or training approaches. Imagine trying to navigate a city without a map – you might eventually get there, but it’ll be much slower and more frustrating.
Methods for Tracking Workout Progress
The key metrics to track are weight lifted, repetitions performed, and sets completed for each exercise. This simple data provides a clear picture of your strength gains over time. For example, if you consistently increase the weight you lift for a specific exercise, or the number of reps you can perform with a given weight, you know you’re making progress.
So you want to pack on some serious muscle, huh? Weight training for weight gain and muscle building is all about smart, consistent effort. Finding the right program is key, and that’s where checking out the best strength training program can really help you maximize your gains. Remember, consistency is king when it comes to sculpting that dream physique – and ditching the excuses!
Conversely, a lack of progress might signal the need for a change in your program. You can use a simple notebook, a spreadsheet, or a dedicated fitness app to log this information.
Measuring Body Composition Changes
While the weights on the bar are important, they don’t tell the whole story. You also need to monitor changes in your body composition – that is, the ratio of muscle mass to body fat. Several methods can be employed to assess this. Body fat percentage can be measured using calipers (a manual method), bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) scales, or DEXA scans (a more sophisticated and accurate method often found in specialized facilities).
Muscle mass can be estimated using BIA scales or DEXA scans. Remember, these measurements provide an overall picture; don’t get hung up on minor fluctuations. Focus on the long-term trends. For example, a consistent decrease in body fat percentage and increase in muscle mass over several weeks or months indicates successful progress.
So, you’re lifting weights to pack on muscle, right? Building a physique that’d make Michelangelo jealous? But what if you’ve got a bit of extra baggage you want to shed? That’s where things get interesting; check out this guide on Designing a strength training workout plan for rapid fat loss to sculpt that dream body.
Then, once you’re lean and mean, you can really focus on adding serious muscle mass!
Strategies for Adjusting the Training Program
Hitting a plateau is inevitable. It’s not a sign of failure; it simply means your body has adapted to your current training stimulus. When progress stalls, it’s time to make adjustments. This might involve increasing the weight lifted, increasing the number of sets or reps, changing the exercises, altering the training split, or incorporating advanced training techniques like drop sets or supersets.
Consider also focusing on proper form and rest. Insufficient rest hinders muscle growth and recovery. Remember, consistency and smart adjustments are key to continued progress. For instance, if you’ve plateaued on your bench press, try incorporating incline or decline variations to target different muscle fibers.
Sample Progress Tracking Sheet
This table provides a simple way to track your progress. Remember to adjust it to fit your specific workout routine.
| Date | Exercise | Weight (kg) | Sets/Reps |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-10-27 | Bench Press | 60 | 3 x 8 |
| 2024-10-27 | Squats | 70 | 3 x 10 |
| 2024-10-28 | Deadlifts | 80 | 1 x 5 |
| 2024-10-29 | Bench Press | 62.5 | 3 x 8 |
| 2024-10-29 | Squats | 72.5 | 3 x 10 |
| 2024-10-30 | Deadlifts | 85 | 1 x 5 |
Addressing Common Challenges and Misconceptions
So, you’ve decided to embark on the glorious journey of building muscle and gaining weight through weight training. Fantastic! But before you start picturing yourself as the next Arnold Schwarzenegger (or, you know, a healthier, stronger version of yourself), let’s tackle some common misconceptions and pitfalls that can trip up even the most dedicated gym-goers. Understanding these challenges will help you navigate the weight room with more confidence and less frustration.
Common Misconceptions About Weight Training for Muscle Growth
Many myths surround muscle building, often leading to frustration and ineffective training. One pervasive myth is that you need to train every muscle group every day. This is a recipe for overtraining and injury, not growth. Another misconception is that lifting lighter weights with more repetitions automatically leads to muscle growth. While high-rep training has its place, focusing solely on it might neglect the strength gains crucial for building muscle mass.
Finally, believing that supplements are a magic bullet is a common fallacy. Supplements can be helpful additions, but they’re no substitute for proper training and nutrition.
The Importance of Proper Warm-up and Cool-down Routines
Think of your body as a finely tuned engine. You wouldn’t rev it to full speed without warming it up first, right? The same applies to your muscles. A proper warm-up, involving light cardio and dynamic stretching (think arm circles, leg swings), prepares your body for the intense workout ahead, increasing blood flow to muscles and reducing the risk of injury.
Conversely, a cool-down, involving static stretching (holding stretches for 20-30 seconds), helps your muscles recover, reducing soreness and stiffness. Ignoring these crucial steps is like ignoring your car’s oil change – eventually, something will break down.
Common Weight Training Injuries and Their Prevention
Weight training, while incredibly beneficial, does carry a risk of injury if proper form and precautions aren’t taken. Lower back pain is a common complaint, often stemming from improper lifting technique during exercises like squats and deadlifts. Solutions include focusing on maintaining a neutral spine, engaging your core muscles, and gradually increasing weight. Another frequent injury is shoulder impingement, often caused by incorrect form during overhead presses or bench presses.
So you want to pack on some serious muscle, huh? Weight training for weight gain and muscle building is all about progressive overload – pushing your limits each workout. But how do you know you’re using the right weight? That’s where figuring out the sweet spot comes in, and this guide on Finding the right weights for strength training and muscle growth can help.
Get the weight right, and watch those gains explode! Remember, consistency and proper form are key to building that dream physique.
Paying close attention to form, maintaining proper posture, and avoiding excessive weight are key preventative measures. Knee injuries can also occur, particularly during squats and lunges. Ensuring proper knee alignment and avoiding excessive weight are crucial. Remember, proper form trumps weight lifted every single time.
Preventing Overtraining
Overtraining is the bane of many a weightlifter’s existence. It’s characterized by persistent fatigue, decreased performance, and increased risk of injury. The key to avoiding overtraining is to allow your body adequate rest and recovery. This means incorporating rest days into your training schedule, prioritizing sleep (aim for 7-9 hours), and listening to your body. Ignoring pain or pushing yourself too hard when feeling fatigued is a surefire way to invite overtraining.
Furthermore, gradually increasing training volume and intensity prevents sudden shocks to the system. Think of it as a marathon, not a sprint. Consistency and patience are your allies here. Remember, muscle growth happens during recovery, not just during the workout.
Visualizing Muscle Growth
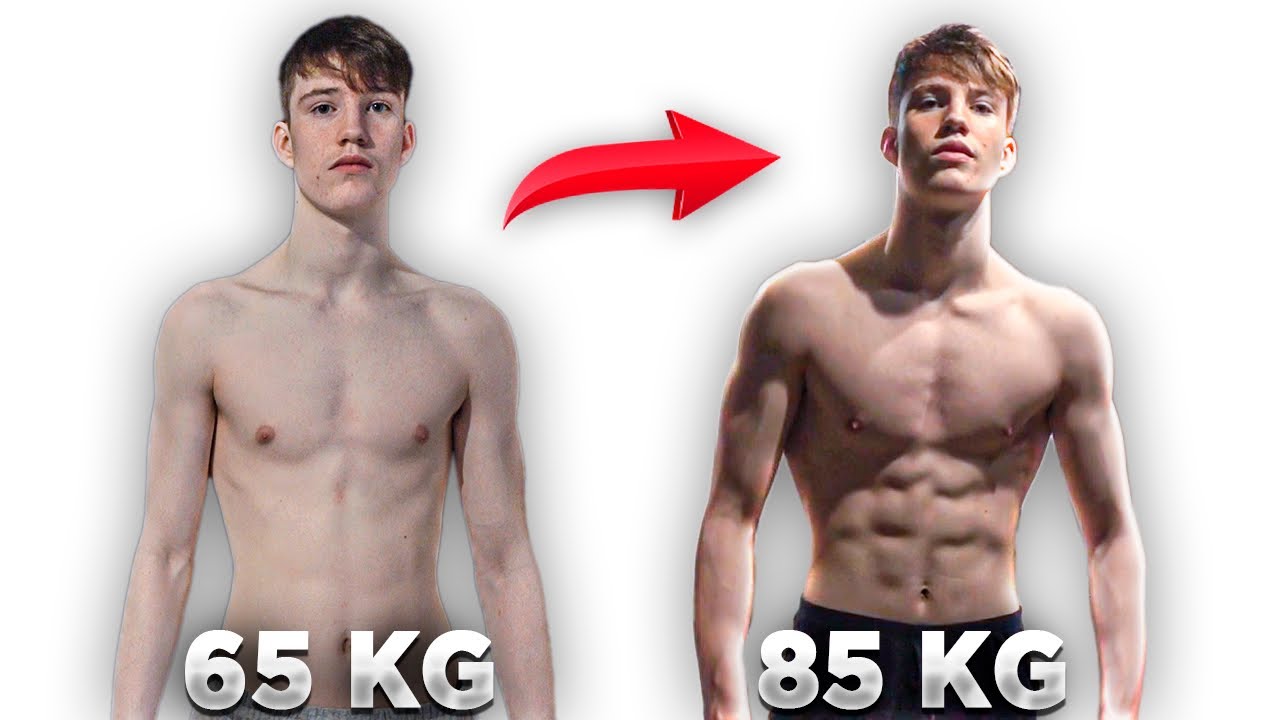
So, you’ve been hitting the iron like a boss, fueling your body with the right nutrients, and following your meticulously crafted weight training program. But when will you start seeing those glorious gains? Let’s delve into the visual spectacle of muscle growth – a transformation that’s as rewarding as it is visually stunning. Prepare to be amazed (and maybe a little bit sore).Visual changes during a well-structured weight training program aren’t instantaneous; they unfold gradually, like a magnificent muscle-bound time-lapse.
Think of it as a slow-motion superhero origin story, but instead of a radioactive spider bite, it’s heavy squats and bench presses. The changes will be subtle at first, but as weeks turn into months, you’ll start noticing significant shifts in your physique. This isn’t about becoming a bodybuilder overnight; it’s about consistent progress and celebrating those hard-earned gains.
Changes in Muscle Size and Definition
Initially, you might notice a slight increase in muscle fullness, particularly in areas you’ve been targeting. Your biceps, for example, might feel a bit firmer, and you might notice a subtle increase in their circumference. As you progress, this fullness will become more pronounced. Imagine your biceps, previously relatively flat, now exhibiting a noticeable roundness and a slight bulge.
This increased size is due to hypertrophy – the increase in the size of your muscle fibers.In your legs, you might notice your quads becoming more defined, with the individual muscle heads becoming more visible. Your calves might look fuller and more sculpted. Your chest will gain width and thickness, creating a more powerful, broad-shouldered look. The latissimus dorsi (lats) in your back will develop a more V-shaped appearance, giving you that coveted “broad back” physique.
Your shoulders will appear broader and rounder, adding to your overall muscularity.As you continue training, you’ll observe not only increased size but also enhanced definition. This improved definition is the result of a decrease in body fat, allowing the muscles to stand out more prominently. Imagine your abdominal muscles, once hidden beneath a layer of fat, now clearly visible as a series of defined lines – the reward for your dedication to both weight training and nutrition.
The veins in your arms and legs might become more prominent, another visual indicator of muscle growth and reduced body fat.Think of it like this: your muscles start as soft clay, then slowly begin to harden and take shape. Over time, that clay is sculpted into a masterpiece of strength and definition, each muscle group revealing its intricate details.
It’s a testament to your commitment, your effort, and your ability to transform your body through consistent, focused training.
Visual Changes in Specific Muscle Groups
Let’s take a closer look at the visual transformations you can expect in key muscle groups. For example, your biceps, initially relatively slender, will gain significant size and definition. Imagine the change from a relatively straight line to a noticeable peak at the top of the bicep, with the muscle bulging noticeably when flexed. This visual change isn’t just about size; it’s about the improved shape and contour of the muscle.Your chest will transition from relatively flat to fuller and wider, with the pectoral muscles becoming more defined, particularly along the midline.
You might notice a more pronounced separation between the pectoral muscles, known as the “pec tear,” which further enhances the visual appeal of the chest.Your back, initially perhaps quite flat, will develop a thicker, more V-shaped appearance. The lats will become more prominent, creating a broader and more powerful look. The detail in the back muscles will increase, making the muscles more visible even when not actively flexed.Your legs, a large muscle group, will exhibit changes in both size and definition.
The quads will gain significant mass, becoming fuller and more defined. The individual muscle heads will become more visible, creating a more sculpted look. The hamstrings, located at the back of your thighs, will also increase in size, adding to the overall muscularity of your legs. The calves will appear fuller and more defined, adding to the overall aesthetic appeal of your legs.
Closing Notes

So, there you have it: your comprehensive guide to conquering the world of weight training for weight gain and muscle building. Remember, consistency is key. Don’t expect overnight miracles; building muscle takes time, dedication, and a healthy dose of patience. But with a well-structured plan, the right nutrition, and a dash of unwavering determination, you’ll be amazed at what your body can achieve.
Now go forth and unleash your inner muscle-bound marvel!
